Page 17 - Drilling Technology in Nontechnical Language
P. 17
8 Drilling Technology in Nontechnical Language Second Edition
These shales will swell and become soft, like unset putty. Sticky clays will
fill the hole, and if the drillstring becomes stuck, the hole could be lost.
Other shale types can be very stable in the presence of water and are not
difficult to drill through with water-based drilling fluids (called drilling
muds). In practice, a shale formation may consist of a mixture of different
clay mineral types, so the reactivity of shale to water can vary from mild
to severe. Chemicals are usually added to the drilling fluid to decrease
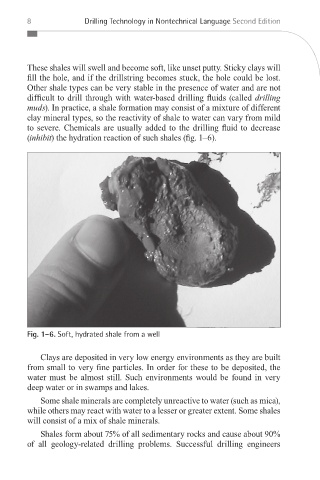
(inhibit) the hydration reaction of such shales (fig. 1–6).
Fig. 1–6. Soft, hydrated shale from a well
Clays are deposited in very low energy environments as they are built
from small to very fine particles. In order for these to be deposited, the
water must be almost still. Such environments would be found in very
deep water or in swamps and lakes.
Some shale minerals are completely unreactive to water (such as mica),
while others may react with water to a lesser or greater extent. Some shales
will consist of a mix of shale minerals.
Shales form about 75% of all sedimentary rocks and cause about 90%
of all geology-related drilling problems. Successful drilling engineers
_Devereux_Book.indb 8 1/16/12 2:06 PM