Page 38 - Dust Explosions in the Process Industries
P. 38
Dust Explosions: An Overview 1 7
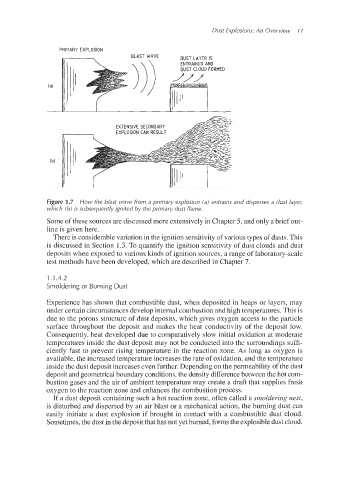
PRIMARY EXPLOSION
DUST LAYER IS
ENTRAINED AND
DUST CLOUD FORMED
EXTENSIVE SECO
EXPLOSION CAN
ibl
Figure 1.7 How the blast wave from a primary explosion (a) entrains and disperses a dust layer,
which (b) is subsequently ignited by the primary dust flame.
Some of these sources are discussed more extensively in Chapter 5, and only a brief out-
line is given here.
There is considerable variation in the ignition sensitivity of various types of dusts. This
is discussed in Section 1.3. To quantify the ignition sensitivity of dust clouds and dust
deposits when exposed to various kinds of ignition sources, a range of laboratory-scale
test methods have been developed, which are described in Chapter 7.
1.I .4.2
Smoldering or Burning Dust
Experience has shown that combustible dust, when deposited in heaps or layers, may
under certain circumstances develop internal combustion and high temperatures. This is
due to the porous structure of dust deposits, which gives oxygen access to the particle
surface throughout the deposit and makes the heat conductivity of the deposit low.
Coinsequently, heat developed due to comparatively slow initial oxidation at moderate
temperatures inside the dust deposit may not be conducted into the surroundings suffi-
cieiitly fast to prevent rising temperature in the reaction zone. As long as oxygen is
available, the increased temperature increases the rate of oxidation, and the temperature
inside the dust deposit increases even further. Depending on the permeability of the dust
deposit and geometrical boundary conditions, the density difference between the hot com-
bustion gases and the air of ambient temperature may create a draft that supplies fresh
oxygen to the reaction zone and enhances the combustion process.
If a dust deposit containing such a hot reaction zone, often called a smoldering nest,
is disturbed and dispersed by an air blast or a mechanical action, the burning dust can
easily initiate a dust explosion if brought in contact with a combustible dust cloud.
Sometimes,the dust in the deposit that has not yet burned, forms the explosible dust cloud.