Page 535 - Dust Explosions in the Process Industries
P. 535
502 Dust Explosions in the Process Industries
112 mm
HEATING (1500 W)
TEST CHAMBER
0
THERMO-
COUPLE RUBBER BULB
Lomm+
MEASURING I
THERMOCOUPLE
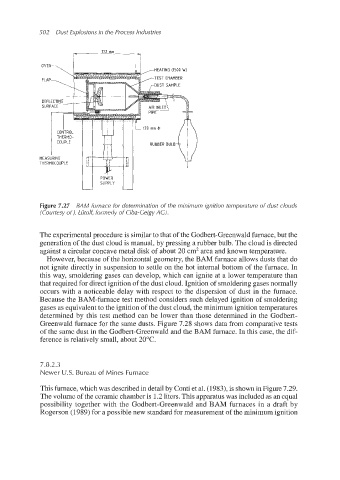
Figure 7.27 BAM furnace for determination of the minimum ignition temperature of dust clouds
(Courtesy of 1. Liitolf,formerly of Ciba-GeigyAC).
The experimentalprocedure is similar to that of the Godbert-Greenwaldfurnace,but the
generation of the dust cloud is manual, by pressing a rubber bulb. The cloud is directed
against a circular concave metal disk of about 20 cm2area and known temperature.
However, because of the horizontal geometry, the BAM furnace allows dusts that do
not ignite directly in suspension to settle on the hot internal bottom of the furnace. In
this way, smoldering gases can develop, which can ignite at a lower temperature than
that required for direct ignition of the dust cloud. Ignition of smoldering gases normally
occurs with a noticeable delay with respect to the dispersion of dust in the furnace.
Because the BAM-furnace test method considers such delayed ignition of smoldering
gases as equivalentto the ignition of the dust cloud, the minimum ignition temperatures
determined by this test method can be lower than those determined in the Godbert-
Greenwald furnace for the same dusts. Figure 7.28 shows data from comparative tests
of the same dust in the Godbert-Greenwald and the BAM furnace. In this case, the dif-
ference is relatively small, about 20°C.
7.8.2.3
Newer U.S. Bureau of Mines Furnace
This furnace, which was described in detail by Conti et al. (1983),is shown in Figure 7.29.
The volume of the ceramic chamber is 1.2liters. This apparatus was included as an equal
possibility together with the Godbert-Greenwald and BAM furnaces in a draft by
Rogerson (1989)for a possible new standard for measurement of the minimum ignition