Page 717 - Dust Explosions in the Process Industries
P. 717
684 Dust Explosions in the Process Industries
A.1.2.7
Minimum Ignition Energy (MIE)
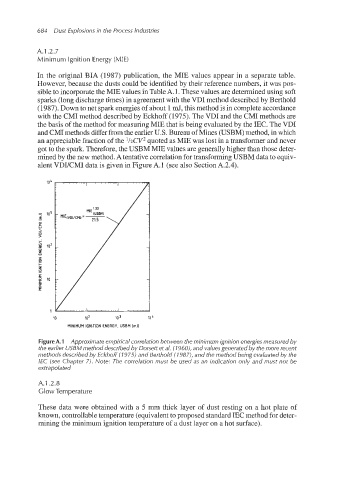
In the original BIA (1987) publication, the MIE values appear in a separate table.
However, because the dusts could be identified by their reference numbers, it was pos-
sible to incorporatethe MIE values in TableA. 1.These values are determined using soft
sparks (long discharge times) in agreement with the VDI method describedby Berthold
(1987). Down to net spark energies of about 1 mJ, this method is in complete accordance
with the CMI method described by Eckhoff (1975). The VDI and the CMI methods are
the basis of the method for measuring MIE that is being evaluated by the IEC. The VDI
and CMI methods differ from the earlier U.S. Bureau of Mines (USBM) method, in which
an appreciablefraction of the l/2CV2 quoted as MIE was lost in a transformer and never
got to the spark. Therefore, the USBM MIE values are generally higher than those deter-
mined by the new method.A tentativecorrelation for transforming USBM data to equiv-
alent VDUCMI data is given in Figure A.1 (see also SectionA.2.4).
f 10
E
f
1
10 102 103 1oL
MINIMUM IGNITION ENERGY, USBM lmJl
Figure A.l Approximate empirical correlation between the minimum ignition energies measured by
the earlier USBM method describedby Dorsett et al. (1 9601, and valuesgenerated by the more recent
methods described by Eckhoff (7 975) and Berthold (I 9871, and the method being evaluated by the
IEC (see Chapter 7). Note: The correlation must be used as an indication only and must not be
extrapolated
A.1.2.8
Glow Temperature
These data were obtained with a 5 mm thick layer of dust resting on a hot plate of
known, controllable temperature (equivalent to proposed standard IEC method for deter-
mining the minimum ignition temperature of a dust layer on a hot surface).