Page 18 - Dynamic Loading and Design of Structures
P. 18
Page 6
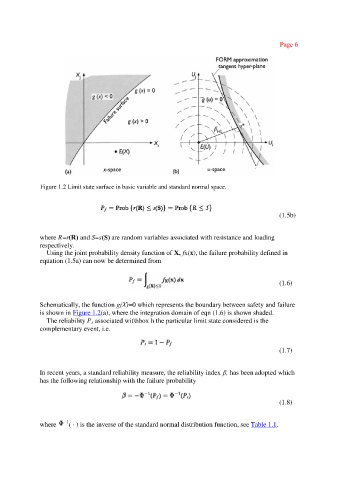
Figure 1.2 Limit state surface in basic variable and standard normal space.
(1.5b)
where R=r(R) and S=s(S) are random variables associated with resistance and loading
respectively.
Using the joint probability density function of X, fx(x), the failure probability defined in
equation (1.5a) can now be determined from
(1.6)
Schematically, the function g(X)=0 which represents the boundary between safety and failure
is shown in Figure 1.2(a), where the integration domain of eqn (1.6) is shown shaded.
The reliability Ps associated wit\hbox h the particular limit state considered is the
complementary event, i.e.
(1.7)
In recent years, a standard reliability measure, the reliability index βhas been adopted which
,
has the following relationship with the failure probability
(1.8)
where −1 ( · ) is the inverse of the standard normal distribution function, see Table 1.1.