Page 263 - Dynamic Loading and Design of Structures
P. 263
Page 234
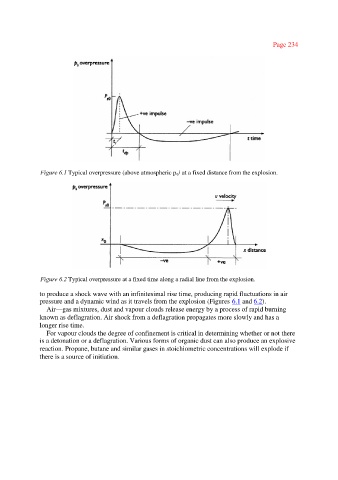
Figure 6.1 Typical overpressure (above atmospheric po) at a fixed distance from the explosion.
Figure 6.2 Typical overpressure at a fixed time along a radial line from the explosion.
to produce a shock wave with an infinitesimal rise time, producing rapid fluctuations in air
pressure and a dynamic wind as it travels from the explosion (Figures 6.1 and 6.2).
Air—gas mixtures, dust and vapour clouds release energy by a process of rapid burning
known as deflagration. Air shock from a deflagration propagates more slowly and has a
longer rise time.
For vapour clouds the degree of confinement is critical in determining whether or not there
is a detonation or a deflagration. Various forms of organic dust can also produce an explosive
reaction. Propane, butane and similar gases in stoichiometric concentrations will explode if
there is a source of initiation.