Page 215 - Dynamics and Control of Nuclear Reactors
P. 215
214 CHAPTER 16 Nuclear plant instrumentation
16.2 Sensor characteristics
16.2.1 Neutron and gamma ray detectors
Since neutrons have no electrical charge, they cannot be detected directly. Rather,
detectors contain material that undergoes reactions with neutrons and releases
charged reaction products or light that can be detected.
In some sensors, charged particles create a measurable electrical current in detec-
tors that maintain a voltage difference between conductors. The sensor’s calibration
converts the measured current into neutron flux.
In some sensors, the charged particle migrates from its source to a metallic
sheath, causing a measurable voltage. The sensor’s calibration converts the measured
voltage into neutron flux.
In some sensors, the neutron interaction produces light. The light intensity can be
measured, and calibration is used to convert the measured light intensity into
neutron flux.
Another measurement of reactor power uses ex-core monitoring of radionuclides
produced in the core by neutron absorption.
Reactor power can also be measured by sensing temperature changes due to
gamma ray heating inside a sheathed probe.
No single detector can satisfy all of the requirements for measuring reactor
power. Three different detectors are used to cover the full range of reactor power:
startup, mid-range and full power. Ex-core sensors provide total power measure-
ments and in-core detectors monitor local power.
Brief descriptions of various detector types are as follows:
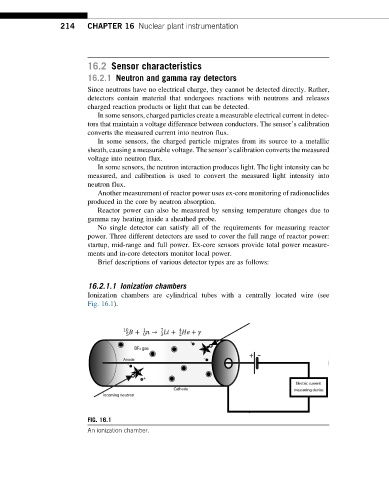
16.2.1.1 Ionization chambers
Ionization chambers are cylindrical tubes with a centrally located wire (see
Fig. 16.1).
FIG. 16.1
An ionization chamber.