Page 252 - Electrical Engineering Dictionary
P. 252
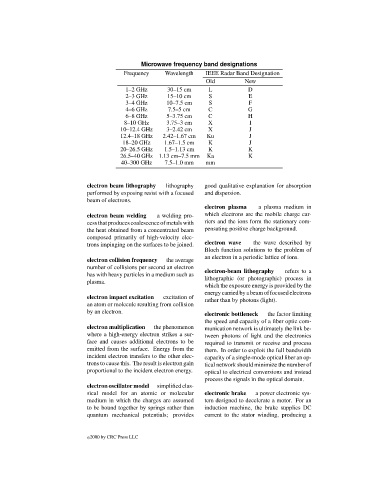
Microwave frequency band designations
Frequency Wavelength IEEE Radar Band Designation
Old New
1–2 GHz 30–15 cm L D
2–3 GHz 15–10 cm S E
3–4 GHz 10–7.5 cm S F
4–6 GHz 7.5–5 cm C G
6–8 GHz 5–3.75 cm C H
8–10 GHz 3.75–3 cm X I
10–12.4 GHz 3–2.42 cm X J
12.4–18 GHz 2.42–1.67 cm Ku J
18–20 GHz 1.67–1.5 cm K J
20–26.5 GHz 1.5–1.13 cm K K
26.5–40 GHz 1.13 cm–7.5 mm Ka K
40–300 GHz 7.5–1.0 mm mm
electron beam lithography lithography good qualitative explanation for absorption
performed by exposing resist with a focused and dispersion.
beam of electrons.
electron plasma a plasma medium in
electron beam welding a welding pro- which electrons are the mobile charge car-
cess that produces coalescence of metals with riers and the ions form the stationary com-
the heat obtained from a concentrated beam pensating positive charge background.
composed primarily of high-velocity elec-
trons impinging on the surfaces to be joined. electron wave the wave described by
Bloch function solutions to the problem of
an electron in a periodic lattice of ions.
electron collision frequency the average
number of collisions per second an electron
electron-beam lithography refers to a
has with heavy particles in a medium such as
lithographic (or photographic) process in
plasma.
which the exposure energy is provided by the
energy carried by a beam of focused electrons
electron impact excitation excitation of
rather than by photons (light).
an atom or molecule resulting from collision
by an electron.
electronic bottleneck the factor limiting
the speed and capacity of a fiber optic com-
electron multiplication the phenomenon munication network is ultimately the link be-
where a high-energy electron strikes a sur- tween photons of light and the electronics
face and causes additional electrons to be required to transmit or receive and process
emitted from the surface. Energy from the them. In order to exploit the full bandwidth
incident electron transfers to the other elec- capacity of a single-mode optical fiber an op-
trons to cause this. The result is electron gain tical network should minimize the number of
proportional to the incident electron energy. optical to electrical conversions and instead
process the signals in the optical domain.
electron oscillator model simplified clas-
sical model for an atomic or molecular electronic brake a power electronic sys-
medium in which the charges are assumed tem designed to decelerate a motor. For an
to be bound together by springs rather than induction machine, the brake supplies DC
quantum mechanical potentials; provides current to the stator winding, producing a
c
2000 by CRC Press LLC