Page 26 - Electrical Installation in Hazardous Area
P. 26
Introduction 5
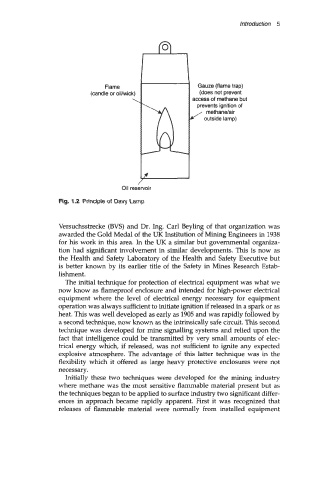
Flame Gauze (flame trap)
(candle or oil/wick) (does not prevent
\ access of methane but
prevents ignition of
methane/ai r
k/ outside lamp)
oil reservoir
Fig. 1.2 Principle of Davy Lamp
Versuchsstrecke (BVS) and Dr. Ing. Carl Beyling of that organization was
awarded the Gold Medal of the UK Institution of Mining Engineers in 1938
for his work in this area. In the UK a similar but governmental organiza-
tion had significant involvement in similar developments. This is now as
the Health and Safety Laboratory of the Health and Safety Executive but
is better known by its earlier title of the Safety in Mines Research Estab-
lishment.
The initial technique for protection of electrical equipment was what we
now know as flameproof enclosure and intended for high-power electrical
equipment where the level of electrical energy necessary for equipment
operation was always sufficient to initiate ignition if released in a spark or as
heat. This was well developed as early as 1905 and was rapidly followed by
a second technique, now known as the intrinsically safe circuit. This second
technique was developed for mine signalling systems and relied upon the
fact that intelligence could be transmitted by very small amounts of elec-
trical energy which, if released, was not sufficient to ignite any expected
explosive atmosphere. The advantage of this latter technique was in the
flexibility which it offered as large heavy protective enclosures were not
necessary.
Initially these two techniques were developed for the mining industry
where methane was the most sensitive flammable material present but as
the techniques began to be applied to surface industry two significant differ-
ences in approach became rapidly apparent. First it was recognized that
releases of flammable material were normally from installed equipment