Page 21 - Electrical Safety of Low Voltage Systems
P. 21
Basic Definitions and Nomenclature 3
1.2.11 Extraneous-Conductive-Part (EXCP)
EXCP is a conductive part, not forming part of the electrical system,
which can be touched, and is liable to introduce a “zero” potential
(i.e., earth potential) or an arbitrary potential. Both of these potentials
are dangerous.
Examples of EXCPs are the metalwork for gas, water, and heating
systems, the metallic frame of a building, conductive floors, walls, etc.
1.2.12 Functional Insulation
It is the insulation between conductive parts at different potentials
that is necessary only for the proper functioning of the appliance.
1.2.13 Ground
The earth, that is to say, a conductive mass whose potential is conven-
tionally considered as zero.
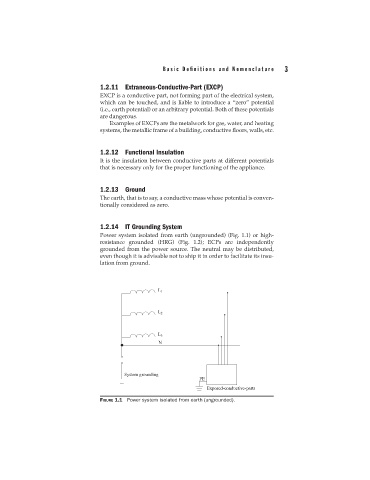
1.2.14 IT Grounding System
Power system isolated from earth (ungrounded) (Fig. 1.1) or high-
resistance grounded (HRG) (Fig. 1.2); ECPs are independently
grounded from the power source. The neutral may be distributed,
even though it is advisable not to ship it in order to facilitate its insu-
lation from ground.
FIGURE 1.1 Power system isolated from earth (ungrounded).