Page 125 - Electronic Commerce
P. 125
Chapter 2
But more important, mobile phones are giving large numbers of people in developing
countries their first access to the online world.
100 Although mobile phones were originally designed to handle voice communications,
they have always been able to transmit data. However, their data transmission speeds
were very low, ranging from 10 to 384 Kbps. Most mobile telephone networks today use
one of a series of technologies called third-generation (3G) wireless technology that offer
download speeds up to 2 Mbps and upload speeds up to 800 Kbps. However, the major
U.S. wireless carriers are rapidly introducing newer technologies, including Long Term
Evolution (LTE) and Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access (WiMAX), that
are generally referred to as fourth-generation (4G) wireless technology. These 4G
technologies offer download speeds up to 14 Mbps and upload speeds up to 8 Mbps.
Most tablet devices, mobile phones, and smartphones have the ability to use either a
mobile telephone network or a locally available wireless network. These devices almost all
have the ability to switch automatically to a wireless network when one is available. Using
a local wireless network can be less expensive than using a mobile telephone network.
As you learned in Chapter 1, companies have seen great potential for these wireless
networks and the devices connected to them in the development of mobile commerce.
You will learn more about revenue models that use wireless technologies in Chapter 3 and
cost-reduction strategies that use wireless technologies in Chapter 5. Chapter 6 includes
an overview of mobile commerce and its future directions. In Chapter 11, you will learn
how some companies are using these mobile technologies to process online payments for
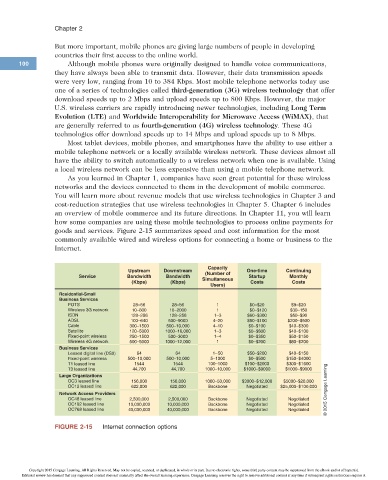
goods and services. Figure 2-15 summarizes speed and cost information for the most
commonly available wired and wireless options for connecting a home or business to the
Internet.
Capacity
Upstream Downstream One-time Continuing
(Number of
Service Bandwidth Bandwidth Simultaneous Startup Monthly
(Kbps) (Kbps) Costs Costs
Users)
Residential-Small
Business Services
POTS 28–56 28–56 1 $0–$20 $9–$20
Wireless 3G network 10–800 10–2000 1 $0–$120 $30–150
ISDN 128–256 128–256 1–3 $60–$300 $50–$90
ADSL 100–640 500–9000 4–20 $50–$100 $200–$500
Cable 300–1500 500–10,000 4–10 $0–$100 $40–$300
Satellite 120–5000 1000–16,000 1–3 $0–$800 $40–$100
Fixed-point wireless 250–1500 500–3000 1–4 $0–$350 $50–$150
Wireless 4G network 500–5000 1000–12,000 1 $0–$200 $80–$200
Business Services
Leased digital line (DS0) 64 64 1–50 $50–$200 $40–$150
Fixed-point wireless 500–10,000 500–10,000 5–1000 $0–$500 $150–$4000
T1 leased line 1544 1544 100–1000 $100–$2000 $300–$1600
T3 leased line 44,700 44,700 1000–10,000 $1000–$9000 $1000–$9000
Large Organizations Learning
OC3 leased line 156,000 156,000 1000–50,000 $3000–$12,000 $5000–$20,000
OC12 leased line 622,000 622,000 Backbone Negotiated $25,000–$100,000
Network Access Providers Cengage
OC48 leased line 2,500,000 2,500,000 Backbone Negotiated Negotiated
OC192 leased line 10,000,000 10,000,000 Backbone Negotiated Negotiated 2015
OC768 leased line 40,000,000 40,000,000 Backbone Negotiated Negotiated
©
FIGURE 2-15 Internet connection options
Copyright 2015 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.