Page 318 - Electronic Commerce
P. 318
Social Networking, Mobile Commerce, and Online Auctions
Reverse (Seller-Bid) Auctions
In a reverse auction (also called a seller-bid auction), multiple sellers submit price bids to
an auctioneer who represents a single buyer. The bids are for a given amount of a specific
item that the buyer wants to purchase. The prices go down as the bidding continues until
no seller is willing to bid lower. Most reverse auctions involve businesses as buyers and
sellers. In many business reverse auctions, the buyer acts as auctioneer and screens
sellers before they can participate. You will learn more about specific implementations of
reverse auctions later in this chapter.
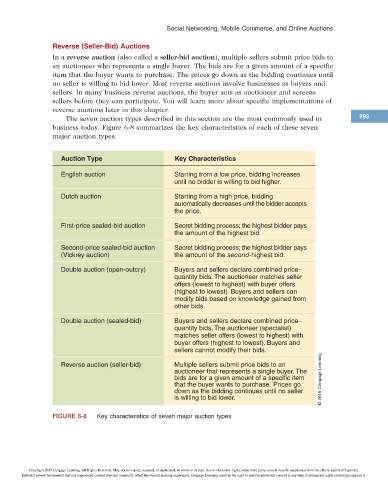
The seven auction types described in this section are the most commonly used in 293
business today. Figure 6-8 summarizes the key characteristics of each of these seven
major auction types.
Auction Type Key Characteristics
English auction Starting from a low price, bidding increases
until no bidder is willing to bid higher.
Dutch auction Starting from a high price, bidding
automatically decreases until the bidder accepts
the price.
First-price sealed-bid auction Secret bidding process; the highest bidder pays
the amount of the highest bid.
Second-price sealed-bid auction Secret bidding process; the highest bidder pays
(Vickrey auction) the amount of the second-highest bid.
Double auction (open-outcry) Buyers and sellers declare combined price–
quantity bids. The auctioneer matches seller
offers (lowest to highest) with buyer offers
(highest to lowest). Buyers and sellers can
modify bids based on knowledge gained from
other bids.
Double auction (sealed-bid) Buyers and sellers declare combined price–
quantity bids. The auctioneer (specialist)
matches seller offers (lowest to highest) with
buyer offers (highest to lowest). Buyers and
sellers cannot modify their bids.
Learning
Reverse auction (seller-bid) Multiple sellers submit price bids to an
auctioneer that represents a single buyer. The
bids are for a given amount of a specific item Cengage
that the buyer wants to purchase. Prices go
down as the bidding continues until no seller
is willing to bid lower. 2015
©
FIGURE 6-8 Key characteristics of seven major auction types
Copyright 2015 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.