Page 247 - Encyclopedia of Business and Finance
P. 247
eobf_E 7/5/06 3:00 PM Page 224
Economics
Labor (Human Resources). Labor is the general category
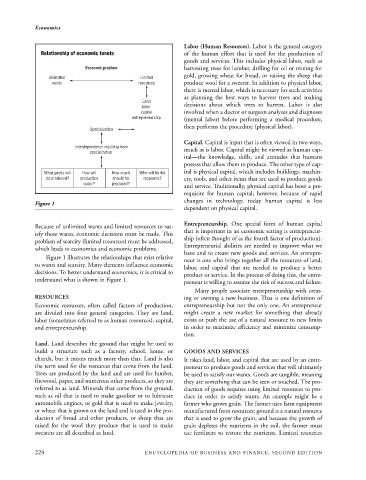
Relationship of economic tenets of the human effort that is used for the production of
goods and services. This includes physical labor, such as
Economic problem harvesting trees for lumber, drilling for oil or mining for
gold, growing wheat for bread, or raising the sheep that
Unlimited Limited
wants resources produce wool for a sweater. In addition to physical labor,
there is mental labor, which is necessary for such activities
as planning the best ways to harvest trees and making
Land
labor decisions about which trees to harvest. Labor is also
capital involved when a doctor or surgeon analyzes and diagnoses
entrepreneurship (mental labor) before performing a medical procedure,
then performs the procedure (physical labor).
Specialization
Capital. Capital is input that is often viewed in two ways,
Interdependence resulting from much as is labor. Capital might be viewed as human cap-
specialization
ital—the knowledge, skills, and attitudes that humans
possess that allow them to produce. The other type of cap-
What goods will How will How much Who will be the ital is physical capital, which includes buildings, machin-
be produced? production should be recipients? ery, tools, and other items that are used to produce goods
occur? produced?
and service. Traditionally, physical capital has been a pre-
requisite for human capital; however, because of rapid
changes in technology, today human capital is less
Figure 1
dependent on physical capital.
Entrepreneurship. One special form of human capital
Because of unlimited wants and limited resources to sat-
that is important in an economic setting is entrepreneur-
isfy those wants, economic decisions must be made. This
ship (often thought of as the fourth factor of production).
problem of scarcity (limited resources) must be addressed,
Entrepreneurial abilities are needed to improve what we
which leads to economics and economic problems.
have and to create new goods and services. An entrepre-
Figure 1 illustrates the relationships that exist relative
neur is one who brings together all the resources of land,
to wants and scarcity. Many elements influence economic
labor, and capital that are needed to produce a better
decisions. To better understand economics, it is critical to
product or service. In the process of doing this, the entre-
understand what is shown in Figure 1. preneur is willing to assume the risk of success and failure.
Many people associate entrepreneurship with creat-
RESOURCES ing or owning a new business. That is one definition of
Economic resources, often called factors of production, entrepreneurship but not the only one. An entrepreneur
are divided into four general categories. They are land, might create a new market for something that already
labor (sometimes referred to as human resources), capital, exists or push the use of a natural resource to new limits
and entrepreneurship. in order to maximize efficiency and minimize consump-
tion.
Land. Land describes the ground that might be used to
build a structure such as a factory, school, home, or GOODS AND SERVICES
church, but it means much more than that. Land is also It takes land, labor, and capital that are used by an entre-
the term used for the resources that come from the land. preneur to produce goods and services that will ultimately
Trees are produced by the land and are used for lumber, be used to satisfy our wants. Goods are tangible, meaning
firewood, paper, and numerous other products, so they are they are something that can be seen or touched. The pro-
referred to as land. Minerals that come from the ground, duction of goods requires using limited resources to pro-
such as oil that is used to make gasoline or to lubricate duce in order to satisfy wants. An example might be a
automobile engines, or gold that is used to make jewelry, farmer who grows grain. The farmer uses farm equipment
or wheat that is grown on the land and is used in the pro- manufactured from resources; ground is a natural resource
duction of bread and other products, or sheep that are that is used to grow the grain; and because the growth of
raised for the wool they produce that is used to make grain depletes the nutrients in the soil, the farmer must
sweaters are all described as land. use fertilizers to restore the nutrients. Limited resources
224 ENCYCLOPEDIA OF BUSINESS AND FINANCE, SECOND EDITION