Page 60 - Encyclopedia of Chemical Compounds 3 Vols
P. 60
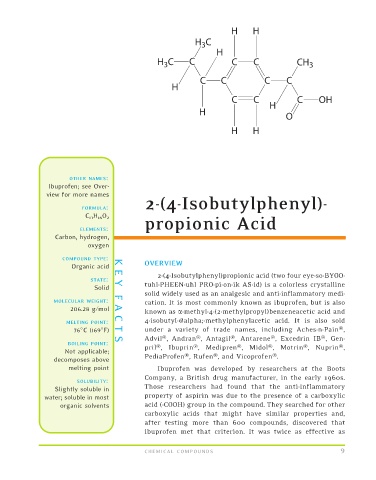
H H
H C
3
H
H C C C C CH 3
3
C C C C
H
C C C OH
H
H
O
H H
OTHER NAMES:
Ibuprofen; see Over-
view for more names
2-(4-Isobutylphenyl)-
FORMULA:
C 13 H 18 O 2
propionic Acid
ELEMENTS:
Carbon, hydrogen,
oxygen
COMPOUND TYPE:
OVERVIEW
Organic acid KE
2-(4-Isobutylphenyl)propionic acid (two four eye-so-BYOO-
STATE:
tuhl-PHEEN-uhl PRO-pi-on-ik AS-id) is a colorless crystalline
Solid
Y
solid widely used as an analgesic and anti-inflammatory medi-
MOLECULAR WEIGHT: F cation. It is most commonly known as ibuprofen, but is also
206.28 g/mol A known as a-methyl-4-(2-methylpropyl)benzeneacetic acid and
MELTING POINT: C 4-isobutyl-@alpha;-methylphenylacetic acid. It is also sold
Ò
76 C (169 F) T under a variety of trade names, including Aches-n-Pain ,
Ò
Ò
Ò
Ò
Ò
Advil , Andran , Antagil , Antarene , Excedrin IB , Gen-
BOILING POINT:
S
Ò
Ò
Ò
Ò
Ò
Ò
pril , Ibuprin , Medipren , Midol , Motrin , Nuprin ,
Not applicable;
Ò
Ò
Ò
PediaProfen , Rufen , and Vicoprofen .
decomposes above
melting point Ibuprofen was developed by researchers at the Boots
Company, a British drug manufacturer, in the early 1960s.
SOLUBILITY:
Those researchers had found that the anti-inflammatory
Slightly soluble in
water; soluble in most property of aspirin was due to the presence of a carboxylic
organic solvents acid (-COOH) group in the compound. They searched for other
carboxylic acids that might have similar properties and,
after testing more than 600 compounds, discovered that
ibuprofen met that criterion. It was twice as effective as
CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS 9