Page 36 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioTechnology
P. 36
P1: GLM Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002G-62 May 19, 2001 19:27
176 Biomaterials, Synthetic Synthesis, Fabrication, and Applications
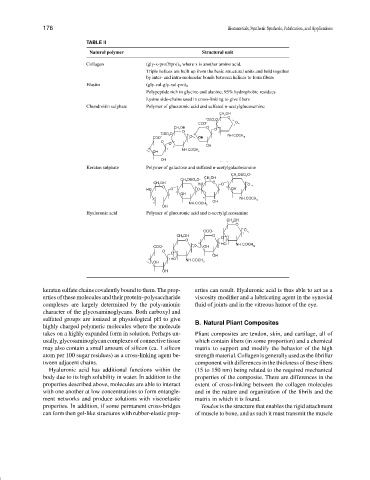
TABLE II
Natural polymer Structural unit
Collagen (gly-x-pro/Hpro) n where x is another amino acid.
Triple helices are built up from the basic structural units and held together
by inter- and intra-molecular bonds between helices to form fibers
Elastin (gly-val-gly-val-pro) n
Polypeptide rich in glycine and alanine, 95% hydrophobic residues
Lysine side-chains used in cross-linking to give fibers
Chondroitin sulphate Polymer of glucuronic acid and sulfated n-acetylglucosamine
Keratan sulphate Polymer of galactose and sulfated n-acetylgalactosamine
Hyaluronic acid Polymer of glucuronic acid and n-acetylglucosamine
keratan sulfate chains covalently bound to them. The prop- erties can result. Hyaluronic acid is thus able to act as a
erties of these molecules and their protein–polysaccharide viscosity modifier and a lubricating agent in the synovial
complexes are largely determined by the poly-anionic fluid of joints and in the vitreous humor of the eye.
character of the glycosaminoglycans. Both carboxyl and
sulfated groups are ionized at physiological pH to give
B. Natural Pliant Composites
highly charged polymeric molecules where the molecule
takes on a highly expanded form in solution. Perhaps un- Pliant composites are tendon, skin, and cartilage, all of
usally, glycosaminoglycan complexes of connective tissue which contain fibers (in some proportion) and a chemical
may also contain a small amount of silicon (ca. 1 silicon matrix to support and modify the behavior of the high
atom per 100 sugar residues) as a cross-linking agent be- strengthmaterial.Collagenisgenerallyusedasthefibrillar
tween adjacent chains. component with differences in the thickness of these fibers
Hyaluronic acid has additional functions within the (15 to 150 nm) being related to the required mechanical
body due to its high solubility in water. In addition to the properties of the composite. There are differences in the
properties described above, molecules are able to interact extent of cross-linking between the collagen molecules
with one another at low concentrations to form entangle- and in the nature and organization of the fibrils and the
ment networks and produce solutions with viscoelastic matrix in which it is found.
properties. In addition, if some permanent cross-bridges Tendon is the structure that enables the rigid attachment
can form then gel-like structures with rubber-elastic prop- of muscle to bone, and as such it must transmit the muscle