Page 44 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Chemical Engineering
P. 44
P1: FJD Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN001-13 May 7, 2001 12:29
266 Adsorption (Chemical Engineering)
For nitrogen production, a carbon molecular sieve ad-
sorbent is generally used. The equilibrium isotherms for
oxygen and nitrogen on carbon molecular sieves are al-
most identical, but the micropore diffusivity of oxygen
∼ 30). A kinetic separation is
is much higher (D O 2 /D N 2
therefore possible, yielding nitrogen as the raffinate prod-
uct. The process could be carried out in a Skarstrom cycle,
but the cycle shown in Fig. 11(b) provides a more attractive
alternative. This system is self-purging because the purge
gas is provided by the residential nitrogen which desorbs
during the “desorption” step. Although high-purity nitro-
gen can be obtained in this way, it is generally more eco-
nomic to produce a nitrogen product of ∼99% purity and
remove the remaining oxygen by hydrogen addition and
catalytic oxidation.
In the zeolite-based PSA process the argon is separated
with the oxygen. For medical applications the presence of
a small amount of argon is of little consequence, but it is
a significant disadvantage for welding since the presence
of even a small amount of argon leads to a significant
reduction of flame temperature and cutting speed. In the
carbon sieve process the argon and nitrogen are separated
together as the raffinate product.
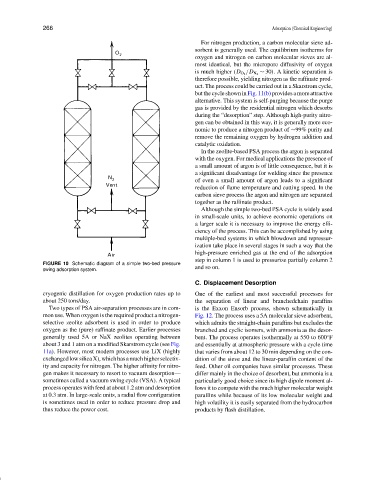
Although the simple two-bed PSA cycle is widely used
in small-scale units, to achieve economic operations on
a larger scale it is necessary to improve the energy effi-
ciency of the process. This can be accomplished by using
multiple-bed systems in which blowdown and repressur-
ization take place in several stages in such a way that the
high-pressure enriched gas at the end of the adsorption
step in column 1 is used to pressurize partially column 2
FIGURE 10 Schematic diagram of a simple two-bed pressure
and so on.
swing adsorption system.
C. Displacement Desorption
cryogenic distillation for oxygen production rates up to One of the earliest and most successful processes for
about 250 tons/day. the separation of linear and branchedchain paraffins
Two types of PSA air-separation processes are in com- is the Exxon Ensorb process, shown schematically in
mon use. When oxygen is the required product a nitrogen- Fig. 12. The process uses a 5A molecular sieve adsorbent,
selective zeolite adsorbent is used in order to produce which admits the straight-chain paraffins but excludes the
oxygen as the (pure) raffinate product. Earlier processes branched and cyclic isomers, with ammonia as the desor-
generally used 5A or NaX zeolites operating between bent. The process operates isothermally at 550 to 600 F
◦
about 3 and 1 atm on a modified Skarstrom cycle (see Fig. and essentially at atmospheric pressure with a cycle time
11a). However, most modern processes use LiX (highly that varies from about 12 to 30 min depending on the con-
exchangedlowsilicaX),whichhasamuchhigherselectiv- dition of the sieve and the linear-paraffin content of the
ity and capacity for nitrogen. The higher affinity for nitro- feed. Other oil companies have similar processes. These
gen makes it necessary to resort to vacuum desorption— differ mainly in the choice of desorbent, but ammonia is a
sometimes called a vacuum swing cycle (VSA). A typical particularly good choice since its high dipole moment al-
process operates with feed at about 1.2 atm and desorption lows it to compete with the much higher molecular weight
at 0.3 atm. In large-scale units, a radial flow configuration paraffins while because of its low molecular weight and
is sometimes used in order to reduce pressure drop and high volatility it is easily separated from the hydrocarbon
thus reduce the power cost. products by flash distillation.