Page 30 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Organic Chemistry
P. 30
P1: GLQ Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN001F-4 May 7, 2001 16:19
82 Acetylene
such as m-nitrobromobenzene with 3-methyl-1-butyn- as a precursor to form m-aminophenylacetylene, which
3-ol (MB), using a catalyst composed of palladious is an important acetylenic capping agent for polyimide
chloride and triphenylphosphine. The catalyst complex polymers. This is an alternative method of preparing the
[PdCl 2 –P–(C 6 H 5 ) 3 ] is further activated with a catalytic m-amino derivative in place of catalytic hydrogenation,
amount of cuprous iodide, used as promoter. The reaction cited above.
◦
is carried out in an amine solvent at 50–100 C. The re-
sulting nitrophenylhydroxyacetylene is then cleaved with
base to the m-nitrophenylacetylene and acetone. The base C. Acetylene-Capped Polyimide Polymers
cleavage can be carried out in situ, and overall yields are, The work of N. Bilow and co-workers under sponsor-
on average, greater than 80%. ship of the U.S. Air Force and Hughes Aircraft Com-
catalyst pany was responsible for novel, acetylene-terminated
Br HC C C (CH 3 ) 2
oligomers that could be cured in the absence of cata-
OH lysts at 200 C to high-strength polymers. These acetylene-
◦
terminated polyimides cured readily without objectional
NO 2
C C C (CH 3 ) 2 evolution of volatiles such as water or alcohol to yield
nonporous, void-free, high-strength polymers stable up to
OH
◦
370 C. Graphitereinforced composites cured with these
NO 2
acetylenic polyimides and subjected to aging in air at
320 C for 1000 hr had 75% of their flexural strength
◦
∆ NaOH
retained. The polymers were also observed to be supe-
rior laminating resins for 6 A1-4V titanium in forming
◦
Η 2 catalyst titanium–titanium bonds stable at 500 F. The initial appli-
C CH (CH 3 ) 2 CO( )
cation of these resins was directed primarily at the aircraft
and aerospace industries.
NO 2
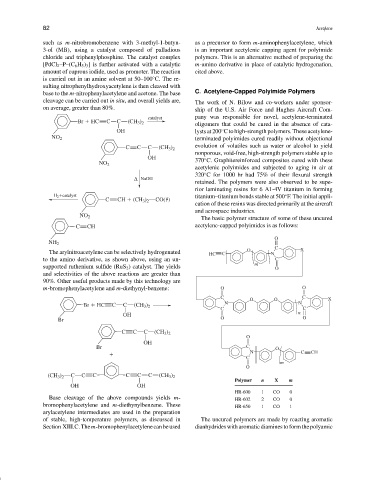
The basic polymer structure of some of these uncured
C CH acetylene-capped polyimides is as follows:
O
NH 2
C X
The arylnitroacetylene can be selectively hydrogenated HC C O N
to the amino derivative, as shown above, using an un- C
m
supported ruthenium sulfide (RuS 2 ) catalyst. The yields O
and selectivities of the above reactions are greater than
90%. Other useful products made by this technology are
m-bromophenylacetylene and m-diethynyl-benzene: O O
C O O C X
Br HC C C (CH 3 ) 2 N N
C C
OH n
Br O O
C C C (CH 3 ) 2
O
OH
Br C O
N C CH
C
m
O
(CH 3 ) 2 C C C C C C (CH 3 ) 2
Polymer n X m
OH OH
HR-600 1 CO 0
Base cleavage of the above compounds yields m- HR-602 2 CO 0
bromophenylacetylene and m-diethynylbenzene. These HR-650 1 CO 1
arylacetylene intermediates are used in the preparation
of stable, high-temperature polymers, as discussed in The uncured polymers are made by reacting aromatic
Section XIII.C.Them-bromophenylacetylenecanbeused dianhydrides with aromatic diamines to form the polyamic