Page 368 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Analytical Chemistry
P. 368
P1: LLL/LOS/GJM P2: GLM Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN0011A-541 July 25, 2001 17:27
Organic Chemistry, Compound Detection 471
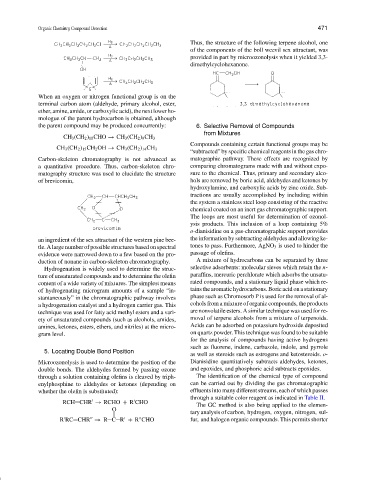
Thus, the structure of the following terpene alcohol, one
of the components of the boll weevil sex attractant, was
provided in part by microozonolysis when it yielded 3,3-
dimethylcyclohexanone.
When an oxygen or nitrogen functional group is on the
terminal carbon atom (aldehyde, primary alcohol, ester,
ether, amine, amide, or carboxylic acid), the next lower ho-
mologue of the parent hydrocarbon is obtained, although
the parent compound may be produced concurrently: 6. Selective Removal of Compounds
from Mixtures
CH 3 (CH 2 ) 10 CHO → CH 3 (CH 2 ) 9 CH 3
Compounds containing certain functional groups may be
CH 3 (CH 2 ) 15 CH 2 OH → CH 3 (CH 2 ) 14 CH 3
“subtracted” by specific chemical reagents in the gas chro-
Carbon-skeleton chromatography is not advanced as matographic pathway. These effects are recognized by
a quantitative procedure. Thus, carbon-skeleton chro- comparing chromatograms made with and without expo-
matography structure was used to elucidate the structure sure to the chemical. Thus, primary and secondary alco-
of brevicomin, hols are removed by boric acid, aldehydes and ketones by
hydroxylamine, and carboxylic acids by zinc oxide. Sub-
tractions are usually accomplished by including within
the system a stainless steel loop consisting of the reactive
chemical coated on an inert gas chromatographic support.
The loops are most useful for determination of ozonol-
ysis products. This inclusion of a loop containing 5%
o-dianisidine on a gas-chromatographic support provides
an ingredient of the sex attractant of the western pine bee- the information by subtracting aldehydes and allowing ke-
tle. A large number of possible structures based on spectral tones to pass. Furthermore, AgNO 3 is used to hinder the
evidence were narrowed down to a few based on the pro- passage of olefins.
duction of nonane in carbon-skeleton chromatography. A mixture of hydrocarbons can be separated by three
Hydrogenation is widely used to determine the struc- selective adsorbents: molecular sieves which retain the n-
ture of unsaturated compounds and to determine the olefin paraffins, mercuric perchlorate which adsorbs the unsatu-
content of a wide variety of mixtures. The simplest means rated compounds, and a stationary liquid phase which re-
of hydrogenating microgram amounts of a sample “in- tains the aromatic hydrocarbons. Boric acid on a stationary
stantaneously” in the chromatographic pathway involves phase such as Chromosorb P is used for the removal of al-
a hydrogenation catalyst and a hydrogen carrier gas. This cohols from a mixture of organic compounds, the products
technique was used for fatty acid methyl esters and a vari- are nonvolatile esters. A similar technique was used for re-
ety of unsaturated compounds (such as alcohols, amides, moval of terpene alcohols from a mixture of terpenoids.
amines, ketones, esters, ethers, and nitriles) at the micro- Acids can be adsorbed on potassium hydroxide deposited
gram level. on quartz powder. This technique was found to be suitable
for the analysis of compounds having active hydrogens
such as fluorene, indene, carbazole, indole, and pyrrole
5. Locating Double Bond Position
as well as steroids such as estrogens and ketosteroids. o-
Microozonolysis is used to determine the position of the Dianisidine quantitatively subtracts aldehydes, ketones,
double bonds. The aldehydes formed by passing ozone and epoxides, and phosphoric acid subtracts epoxides.
through a solution containing olefins is cleaved by triph- The identification of the chemical type of compound
enylphosphine to aldehydes or ketones (depending on can be carried out by dividing the gas chromatographic
whether the olefin is substituted): effluents into many different streams, each of which passes
through a suitable color reagent as indicated in Table II.
RCH CHR → RCHO + R CHO
The GC method is also being applied to the elemen-
O tary analysis of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sul-
R RC CHR → R C R + R CHO fur, and halogen organic compounds. This permits shorter