Page 343 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 343
P1: GNT/GRD P2: GPJ Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN010K-480 July 16, 2001 17:22
Noble-Gas Chemistry 453
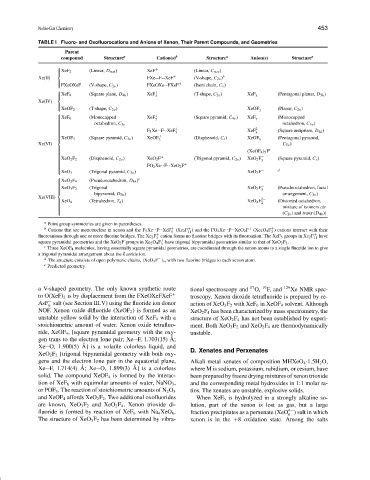
TABLE I Fluoro- and Oxofluorocations and Anions of Xenon, Their Parent Compounds, and Geometries
Parent
compound Structure a Cation(s) b Structure a Anion(s) Structure a
+
XeF 2 (Linear, D ∞h ) XeF (Linear, C ∞v )
Xe(II) FXe--F--XeF + (V-shape, C 2v ) b
FXeOXeF (V-shape, C 2v ) FXeOXe--FXeF (Bent chain, C s )
+
+ −
XeF 4 (Square plane, D 4h ) XeF 3 (T-shape, C 2v ) XeF 5 (Pentagonal planar, D 5h )
Xe(IV)
(T-shape, C 2v ) XeOF − (Planar, C 2v )
XeOF 2 3
XeF 6 (Monocapped XeF + (Square pyramid, C 4v ) XeF − (Monocapped
7
5
octahedron, C 3v )
octahedron, C 3v
+ 2−
F 5 Xe--F--XeF XeF (Square antiprism, D 4d )
5 8
+ −
(Square pyramid, C 4v ) XeOF (Disphenoid, C s ) XeOF (Pentagonal pyramid,
XeOF 4
3 5
Xe(VI) C 5v )
c
(XeOF 4 ) 3 F
−
(Disphenoid, C 2v ) XeO 2 F + (Trigonal pyramid, C 2v ) XeO 2 F (Square pyramid, C s )
XeO 2 F 2
3
FO 2 Xe--F--XeO 2 F +
(Trigonal pyramid, C 3v ) XeO 3 F − d
XeO 3
e
XeO 2 F 4 (Pseudooctahedron, D 4h )
(Trigonal XeO 3 F − (Pseudooctahedron, facial
XeO 3 F 2
3
bipyramid, D 3h ) arrangement, C 3v )
Xe(VIII) 2−
XeO 4 (Tetrahedron, T d ) XeO 4 F 2 (Distorted octahedron,
mixture of isomers cis
(C 2v ) and trans (D 4h ))
a Point group symmetries are given in parentheses.
b Cations that are mononuclear in xenon and the F 5 Xe--F--XeF (Xe 2 F ) and the FO 2 Xe--F--XeO 2 F (Xe 2 O 4 F ) cations interact with their
+
+
+
+
11
3
5
+
fluoroanions through one or more fluorine bridges. The Xe 2 F cation forms no fluorine bridges with its fluoroanion. The XeF 5 groups in Xe 2 F + have
11
3
square pyramidal geometries and the XeO 2 F groups in Xe 2 O 4 F have trigonal bipyramidal geometries similar to that of XeO 2 F 2 .
+
3
c Three XeOF 4 molecules, having essentially square pyramidal geometries, are coordinated through the xenon atoms to a single fluoride ion to give
a trigonal pyramidal arrangement about the fluoride ion.
d The structure consists of open polymeric chains, [XeO 3 F ] n , with two fluorine bridges to each xenon atom.
−
e Predicted geometry.
a V-shaped geometry. The only known synthetic route tional spectroscopy and 17 O, 19 F, and 129 Xe NMR spec-
to O(XeF) 2 is by displacement from the FXeOXeFXeF + troscopy. Xenon dioxide tetrafluoride is prepared by re-
−
AsF salt (see Section III.V) using the fluoride ion donor action of XeO 3 F 2 with XeF 6 in XeOF 4 solvent. Although
6
NOF. Xenon oxide difluoride (XeOF 2 ) is formed as an XeO 2 F 4 has been characterized by mass spectrometry, the
unstable yellow solid by the interaction of XeF 4 with a structure of XeO 2 F 4 has not been established by experi-
stoichiometric amount of water. Xenon oxide tetrafluo- ment. Both XeO 3 F 2 and XeO 2 F 4 are thermodynamically
ride, XeOF 4 , [square pyramidal geometry with the oxy- unstable.
˚
gen trans to the electron lone pair; Xe F, 1.703(15) A;
˚
Xe O, 1.900(5) A] is a volatile colorless liquid, and D. Xenates and Perxenates
XeO 2 F 2 [trigonal bipyramidal geometry with both oxy-
gens and the electron lone pair in the equatorial plane, Alkali metal xenates of composition MHXeO 4 ·1.5H 2 O,
˚
˚
Xe F, 1.714(4) A; Xe O, 1.899(3) A] is a colorless where M is sodium, potassium, rubidium, or cesium, have
solid. The compound XeOF 4 is formed by the interac- been prepared by freeze drying mixtures of xenon trioxide
tion of XeF 6 with equimolar amounts of water, NaNO 3 , and the corresponding metal hydroxides in 1:1 molar ra-
or POF 3 . The reaction of stoichiometric amounts of N 2 O 5 tios. The xenates are unstable, explosive solids.
and XeOF 4 affords XeO 2 F 2 . Two additional oxofluorides When XeF 6 is hydrolyzed in a strongly alkaline so-
are known, XeO 3 F 2 and XeO 2 F 4 . Xenon trioxide di- lution, part of the xenon is lost as gas, but a large
fluoride is formed by reaction of XeF 6 with Na 4 XeO 6 . fraction precipitates as a perxenate (XeO ) salt in which
4−
6
The structure of XeO 3 F 2 has been determined by vibra- xenon is in the +8 oxidation state. Among the salts