Page 86 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Molecular Biology
P. 86
P1: GRB/GRD P2: GNB Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN014F-661 July 28, 2001 20:35
258 Ribozymes
P5
5’ G P4
P1 P2 P3 P6
3í
P8 P7
P9
5’
N’N’N’N’U C AAAA
A 3’
NNNNNG5’
P1 B
5’ AAAA
C
TRANS-SPLICED AAAA
A
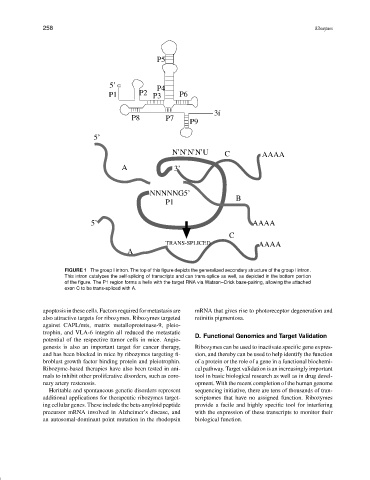
FIGURE 1 The group I intron. The top of this figure depicts the generalized secondary structure of the group I intron.
This intron catalyzes the self-splicing of transcripts and can trans-splice as well, as depicted in the bottom portion
of the figure. The P1 region forms a helix with the target RNA via Watson–Crick base-pairing, allowing the attached
exon C to be trans-spliced with A.
apoptosis in these cells. Factors required for metastasis are mRNA that gives rise to photoreceptor degeneration and
also attractive targets for ribozymes. Ribozymes targeted retinitis pigmentosa.
against CAPL/mts, matrix metalloproteinase-9, pleio-
trophin, and VLA-6 integrin all reduced the metastatic
D. Functional Genomics and Target Validation
potential of the respective tumor cells in mice. Angio-
genesis is also an important target for cancer therapy, Ribozymes can be used to inactivate specific gene expres-
and has been blocked in mice by ribozymes targeting fi- sion, and thereby can be used to help identify the function
broblast growth factor binding protein and pleiotrophin. of a protein or the role of a gene in a functional biochemi-
Ribozyme-based therapies have also been tested in ani- cal pathway. Target validation is an increasingly important
mals to inhibit other proliferative disorders, such as coro- tool in basic biological research as well as in drug devel-
nary artery restenosis. opment. With the recent completion of the human genome
Heritable and spontaneous genetic disorders represent sequencing initiative, there are tens of thousands of tran-
additional applications for therapeutic ribozymes target- scriptomes that have no assigned function. Ribozymes
ing cellular genes. These include the beta-amyloid peptide provide a facile and highly specific tool for interfering
precursor mRNA involved in Alzheimer’s disease, and with the expression of these transcripts to monitor their
an autosomal-dominant point mutation in the rhodopsin biological function.