Page 64 - Subyek Encyclopedia - Encyclopedia of Separation Science
P. 64
Sepsci*21*TSK*Venkatachala=BG
I / CHROMATOGRAPHY 59
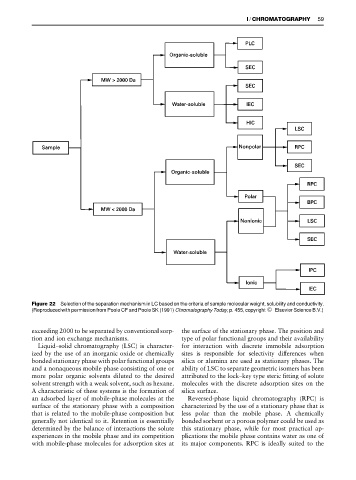
Figure 22 Selection of the separation mechanism in LC based on the criteria of sample molecular weight, solubility and conductivity.
(Reproduced with permission from Poole CF and Poole SK (1991) ChromatographyToday, p. 455, copyright ^ Elsevier Science B.V.)
exceeding 2000 to be separated by conventional sorp- the surface of the stationary phase. The position and
tion and ion exchange mechanisms. type of polar functional groups and their availability
Liquid}solid chromatography (LSC) is character- for interaction with discrete immobile adsorption
ized by the use of an inorganic oxide or chemically sites is responsible for selectivity differences when
bonded stationary phase with polar functional groups silica or alumina are used as stationary phases. The
and a nonaqueous mobile phase consisting of one or ability of LSC to separate geometric isomers has been
more polar organic solvents diluted to the desired attributed to the lock}key type steric Rtting of solute
solvent strength with a weak solvent, such as hexane. molecules with the discrete adsorption sites on the
A characteristic of these systems is the formation of silica surface.
an adsorbed layer of mobile-phase molecules at the Reversed-phase liquid chromatography (RPC) is
surface of the stationary phase with a composition characterized by the use of a stationary phase that is
that is related to the mobile-phase composition but less polar than the mobile phase. A chemically
generally not identical to it. Retention is essentially bonded sorbent or a porous polymer could be used as
determined by the balance of interactions the solute this stationary phase, while for most practical ap-
experiences in the mobile phase and its competition plications the mobile phase contains water as one of
with mobile-phase molecules for adsorption sites at its major components. RPC is ideally suited to the