Page 119 - Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generation
P. 119
102 Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generation
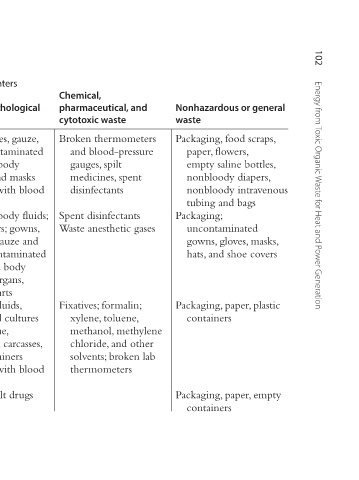
Nonhazardous or general waste Packaging, food scraps, paper, flowers, empty saline bottles, nonbloody diapers, nonbloody intravenous tubing and bags Packaging; uncontaminated gowns, gloves, masks, hats, and shoe covers Packaging, paper, plastic containers Packaging, paper, empty containers
pharmaceutical, and cytotoxic waste Broken thermometers and blood-pressure gauges, spilt medicines, spent disinfectants Spent disinfectants Waste anesthetic gases Fixatives; formalin; xylene, toluene, methanol, methylene chloride, and other solvents; broken lab thermometers
Chemical,
Infectious and pathological waste Dressings, bandages, gauze, and cotton contaminated with blood or body fluids; gloves and masks contaminated with blood or body fluids Blood and other body fluids; suction canisters; gowns, gloves, masks, gauze and other waste contaminated with blood and body fluids;
Major sources of medical waster in hospitals and medical centers
Hypodermic needles, intravenous set needles, broken vials, and ampoules Needles, intravenous sets, scalpels, blades, Needles, broken glass, Petri dishes, slides and cover slips, broken pipettes
Sharps saws
Table 8.1 Location Medical ward Operating theater Laboratory Pharmacy store