Page 126 - Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generation
P. 126
108 Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generation
the medical areas that produce waste, to obtain an initial estimate of the
types and quantities of waste generated, and to understand how the waste is
handled and disposed of. A rapid assessment, combining observations with
interviews and survey questionnaires, should provide sufficient data to iden-
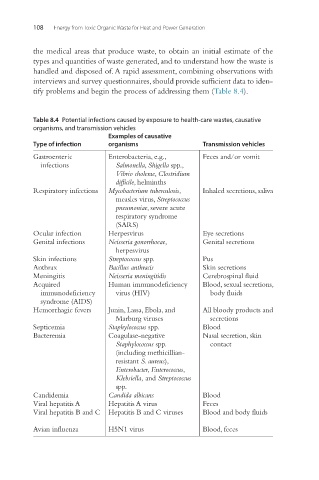
tify problems and begin the process of addressing them (Table 8.4).
Table 8.4 Potential infections caused by exposure to health-care wastes, causative
organisms, and transmission vehicles
Examples of causative
Type of infection organisms Transmission vehicles
Gastroenteric Enterobacteria, e.g., Feces and/or vomit
infections Salmonella, Shigella spp.,
Vibrio cholerae, Clostridium
difficile, helminths
Respiratory infections Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Inhaled secretions, saliva
measles virus, Streptococcus
pneumoniae, severe acute
respiratory syndrome
(SARS)
Ocular infection Herpesvirus Eye secretions
Genital infections Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Genital secretions
herpesvirus
Skin infections Streptococcus spp. Pus
Anthrax Bacillus anthracis Skin secretions
Meningitis Neisseria meningitidis Cerebrospinal fluid
Acquired Human immunodeficiency Blood, sexual secretions,
immunodeficiency virus (HIV) body fluids
syndrome (AIDS)
Hemorrhagic fevers Junin, Lassa, Ebola, and All bloody products and
Marburg viruses secretions
Septicemia Staphylococcus spp. Blood
Bacteremia Coagulase-negative Nasal secretion, skin
Staphylococcus spp. contact
(including methicillian-
resistant S. aureus),
Enterobacter, Enterococcus,
Klebsiella, and Streptococcus
spp.
Candidemia Candida albicans Blood
Viral hepatitis A Hepatitis A virus Feces
Viral hepatitis B and C Hepatitis B and C viruses Blood and body fluids
Avian influenza H5N1 virus Blood, feces