Page 154 - Engineering Plastics Handbook
P. 154
Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS) Resin 127
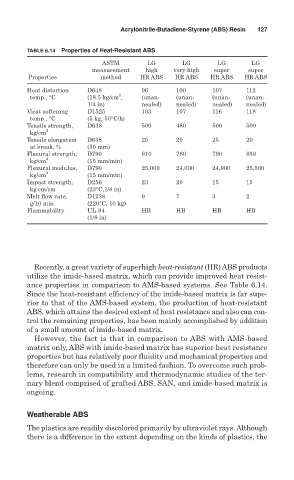
TABLE 6.14 Properties of Heat-Resistant ABS
ASTM LG LG LG LG
measurement high very high super super
Properties method HR ABS HR ABS HR ABS HR ABS
Heat distortion D648 96 100 107 112
2
temp., °C (18.5 kg/cm , (unan- (unan- (unan- (unan-
1/4 in) nealed) nealed) nealed) nealed)
Vicat softening D1525 103 107 116 118
temp., °C (5 kg, 50°C/h)
Tensile strength, D638 500 480 500 500
kg/cm 2
Tensile elongation D638 25 20 25 20
at break, % (50 mm)
Flexural strength, D790 810 780 790 850
kg/cm 2 (15 mm/min)
Flexural modulus, D790 25,000 24,000 24,900 25,500
kg/cm 2 (15 mm/min)
Impact strength, D256 23 20 15 15
kg⋅cm/cm (23°C,1/8 in)
Melt flow rate, D1238 9 7 3 2
g/10 min (220°C, 10 kg)
Flammability UL-94 HB HB HB HB
(1/8 in)
Recently, a great variety of superhigh heat-resistant (HR) ABS products
utilize the imide-based matrix, which can provide improved heat resist-
ance properties in comparison to AMS-based systems. See Table 6.14.
Since the heat-resistant efficiency of the imide-based matrix is far supe-
rior to that of the AMS-based system, the production of heat-resistant
ABS, which attains the desired extent of heat resistance and also can con-
trol the remaining properties, has been mainly accomplished by addition
of a small amount of imide-based matrix.
However, the fact is that in comparison to ABS with AMS-based
matrix only, ABS with imide-based matrix has superior heat resistance
properties but has relatively poor fluidity and mechanical properties and
therefore can only be used in a limited fashion. To overcome such prob-
lems, research in compatibility and thermodynamic studies of the ter-
nary blend comprised of grafted ABS, SAN, and imide-based matrix is
ongoing.
Weatherable ABS
The plastics are readily discolored primarily by ultraviolet rays. Although
there is a difference in the extent depending on the kinds of plastics, the