Page 160 - Engineering Plastics Handbook
P. 160
Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) 133
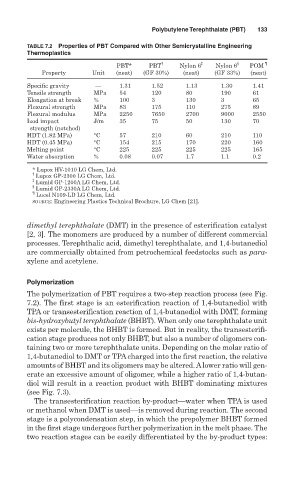
TABLE 7.2 Properties of PBT Compared with Other Semicrystalline Engineering
Thermoplastics
PBT* PBT † Nylon 6 ‡ Nylon 6 § POM ¶
Property Unit (neat) (GF 30%) (neat) (GF 33%) (neat)
Specific gravity — 1.31 1.52 1.13 1.30 1.41
Tensile strength MPa 54 120 80 190 61
Elongation at break % 100 3 130 3 65
Flexural strength MPa 83 175 110 275 89
Flexural modulus MPa 2250 7650 2700 9000 2550
Izod impact J/m 35 75 50 130 70
strength (notched)
HDT (1.82 MPa) °C 57 210 60 210 110
HDT (0.45 MPa) °C 154 215 170 220 160
Melting point °C 225 225 225 225 165
Water absorption % 0.08 0.07 1.7 1.1 0.2
* Lupox HV-1010 LG Chem, Ltd.
†
Lupox GP-2300 LG Chem, Ltd.
‡
Lumid GP-1200A LG Chem, Ltd.
§
Lumid GP-2330A LG Chem, Ltd.
¶
Lucel N109-LD LG Chem, Ltd.
SOURCE: Engineering Plastics Technical Brochure, LG Chem [21].
dimethyl terephthalate (DMT) in the presence of esterification catalyst
[2, 3]. The monomers are produced by a number of different commercial
processes. Terephthalic acid, dimethyl terephthalate, and 1,4-butanediol
are commercially obtained from petrochemical feedstocks such as para-
xylene and acetylene.
Polymerization
The polymerization of PBT requires a two-step reaction process (see Fig.
7.2). The first stage is an esterification reaction of 1,4-butanediol with
TPA or transesterification reaction of 1,4-butanediol with DMT, forming
bis-hydroxybutyl terephthalate (BHBT). When only one terephthalate unit
exists per molecule, the BHBT is formed. But in reality, the transesterifi-
cation stage produces not only BHBT, but also a number of oligomers con-
taining two or more terephthalate units. Depending on the molar ratio of
1,4-butanediol to DMT or TPA charged into the first reaction, the relative
amounts of BHBT and its oligomers may be altered. Alower ratio will gen-
erate an excessive amount of oligomer, while a higher ratio of 1,4-butan-
diol will result in a reaction product with BHBT dominating mixtures
(see Fig. 7.3).
The transesterification reaction by-product—water when TPA is used
or methanol when DMT is used––is removed during reaction. The second
stage is a polycondensation step, in which the prepolymer BHBT formed
in the first stage undergoes further polymerization in the melt phase. The
two reaction stages can be easily differentiated by the by-product types: