Page 166 - Engineering Plastics Handbook
P. 166
Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) 139
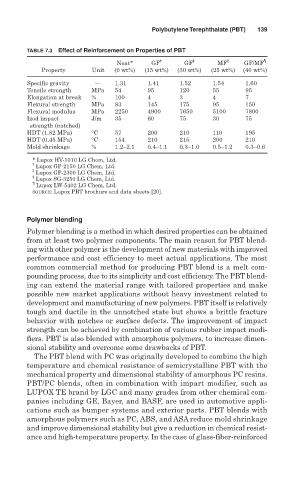
TABLE 7.3 Effect of Reinforcement on Properties of PBT
† ‡ § ¶
Neat* GF GF MF GF/MF
Property Unit (0 wt%) (15 wt%) (30 wt%) (25 wt%) (40 wt%)
Specific gravity — 1.31 1.41 1.52 1.54 1.60
Tensile strength MPa 54 95 120 55 95
Elongation at break % 100 4 3 4 7
Flexural strength MPa 83 145 175 95 150
Flexural modulus MPa 2250 4900 7650 5100 7800
Izod impact J/m 35 60 75 30 75
strength (notched)
HDT (1.82 MPa) °C 57 200 210 110 195
HDT (0.45 MPa) °C 154 210 215 200 210
Mold shrinkage % 1.2–2.1 0.4–1.1 0.3–1.0 0.5–1.2 0.3–0.6
* Lupox HV-1010 LG Chem, Ltd.
†
Lupox GP-2150 LG Chem, Ltd.
‡
Lupox GP-2300 LG Chem, Ltd.
§
Lupox SG-3250 LG Chem, Ltd.
¶
Lupox LW-5402 LG Chem, Ltd.
SOURCE: Lupox PBT brochure and data sheets [20].
Polymer blending
Polymer blending is a method in which desired properties can be obtained
from at least two polymer components. The main reason for PBT blend-
ing with other polymer is the development of new materials with improved
performance and cost efficiency to meet actual applications. The most
common commercial method for producing PBT blend is a melt com-
pounding process, due to its simplicity and cost efficiency. The PBT blend-
ing can extend the material range with tailored properties and make
possible new market applications without heavy investment related to
development and manufacturing of new polymers. PBT itself is relatively
tough and ductile in the unnotched state but shows a brittle fracture
behavior with notches or surface defects. The improvement of impact
strength can be achieved by combination of various rubber impact modi-
fiers. PBT is also blended with amorphous polymers, to increase dimen-
sional stability and overcome some drawbacks of PBT.
The PBT blend with PC was originally developed to combine the high
temperature and chemical resistance of semicrystalline PBT with the
mechanical property and dimensional stability of amorphous PC resins.
PBT/PC blends, often in combination with impart modifier, such as
LUPOX TE brand by LGC and many grades from other chemical com-
panies including GE, Bayer, and BASF, are used in automotive appli-
cations such as bumper systems and exterior parts. PBT blends with
amorphous polymers such as PC, ABS, and ASA reduce mold shrinkage
and improve dimensional stability but give a reduction in chemical resist-
ance and high-temperature property. In the case of glass-fiber-reinforced