Page 97 -
P. 97
Chapter 3 • Enterprise Systems Architecture 73
In server-centric environments, clients only need access to the Internet and a standard
browser (e.g., Internet Explorer or Firefox) with a few plug-ins (e.g., Java Virtual Machine and
others). There are no other user interface applications required on the client; therefore, the client
can be any Internet device that uses such standard Internet technologies as hypertext transport
protocol or hypertext markup language (HTML) for user access, or extensible markup language
for back-end communication between an application and a third-party system with the Internet
application server. The latter falls more under system-to-system integration and is covered in a
later section.
In client-centric environments, client devices will need installation of software develop-
ment kits (SDKs) and proper configuration and integration with client devices for the application
to work properly. This is practically disappearing from PC-based clients due to the advantages
provided by server-centric environments as well as due to higher network bandwidth and
reliability. Client-centric platforms are popular in such other devices as personal digital
assistants (PDAs), Blackberries, and mobile phones that are increasingly used to access informa-
tion from the enterprise systems.
BENEFITS AND DRAWBACKS The key benefit of using the Internet platform as the foundation
is that organizations are able to provide a wide range of end users with access to ERP applica-
tions over the Web as well as more easily integrate their ERP applications with existing internal
systems and external trading partner systems.
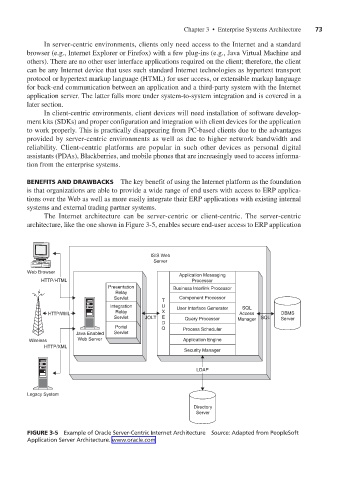
The Internet architecture can be server-centric or client-centric. The server-centric
architecture, like the one shown in Figure 3-5, enables secure end-user access to ERP application
ISIS Web
Server
Web Browser
Application Messaging
HTTP/HTML Processor
Presentation Business Interlink Processor
Relay
Servlet T Component Processor
Integration U User Interface Generator SQL
HTTP/WML Relay X Access DBMS
Servlet JOLT E Query Processor Manager SQL Server
D
Portal O Process Scheduler
Java Enabled Servlet
Wireless Web Server Application Engine
HTTP/XML
Security Manager
LDAP
Legacy System
Directory
Server
FIGURE 3-5 Example of Oracle Server-Centric Internet Architecture Source: Adapted from PeopleSoft
Application Server Architecture. www.oracle.com