Page 177 - Excel Data Analysis
P. 177
10 537547 Ch09.qxd 3/4/03 12:13 PM Page 163
AUTOMATING ACTIONS WITH MACROS 9
UNDERSTANDING VBA (CONTINUED)
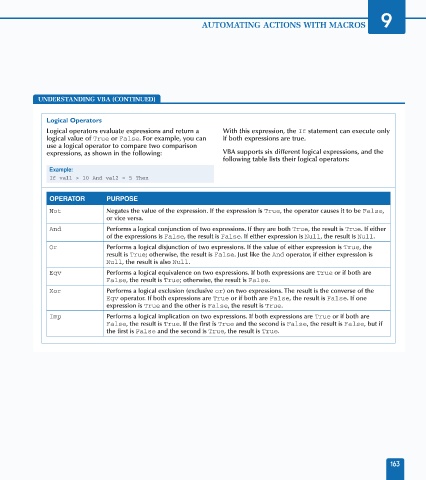
Logical Operators
Logical operators evaluate expressions and return a With this expression, the If statement can execute only
logical value of True or False. For example, you can if both expressions are true.
use a logical operator to compare two comparison
expressions, as shown in the following: VBA supports six different logical expressions, and the
following table lists their logical operators:
Example:
If val1 > 10 And val2 = 5 Then
OPERATOR PURPOSE
Not Negates the value of the expression. If the expression is True, the operator causes it to be False,
or vice versa.
And Performs a logical conjunction of two expressions. If they are both True, the result is True. If either
of the expressions is False, the result is False. If either expression is Null, the result is Null.
Or Performs a logical disjunction of two expressions. If the value of either expression is True, the
result is True; otherwise, the result is False. Just like the And operator, if either expression is
Null, the result is also Null.
Eqv Performs a logical equivalence on two expressions. If both expressions are True or if both are
False, the result is True; otherwise, the result is False.
Xor Performs a logical exclusion (exclusive or) on two expressions. The result is the converse of the
Eqv operator. If both expressions are True or if both are False, the result is False. If one
expression is True and the other is False, the result is True.
Imp Performs a logical implication on two expressions. If both expressions are True or if both are
False, the result is True. If the first is True and the second is False, the result is False, but if
the first is False and the second is True, the result is True.
163