Page 138 - Excel Progamming Weekend Crash Course
P. 138
h540629 ch09.qxd 9/2/03 9:34 AM Page 113
Session 9 — Working with Text 113
String is the string to be converted, and conversion is a constant specifying the con-
version to be performed (see Table 9-4). The function returns the converted string.
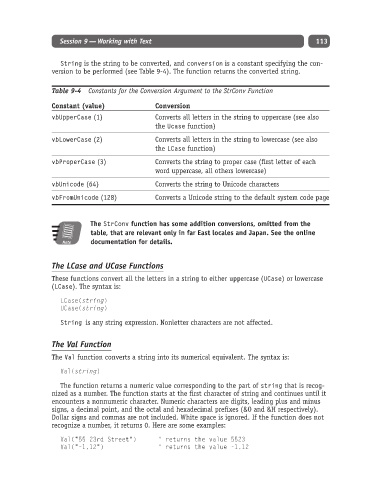
Table 9-4 Constants for the Conversion Argument to the StrConv Function
Constant (value) Conversion
vbUpperCase (1) Converts all letters in the string to uppercase (see also
the Ucase function)
vbLowerCase (2) Converts all letters in the string to lowercase (see also
the LCase function)
vbProperCase (3) Converts the string to proper case (first letter of each
word uppercase, all others lowercase)
vbUnicode (64) Converts the string to Unicode characters
vbFromUnicode (128) Converts a Unicode string to the default system code page
The StrConv function has some addition conversions, omitted from the
table, that are relevant only in far East locales and Japan. See the online
Note documentation for details.
The LCase and UCase Functions
These functions convert all the letters in a string to either uppercase (UCase) or lowercase
(LCase). The syntax is:
LCase(string)
UCase(string)
String is any string expression. Nonletter characters are not affected.
The Val Function
The Val function converts a string into its numerical equivalent. The syntax is:
Val(string)
The function returns a numeric value corresponding to the part of string that is recog-
nized as a number. The function starts at the first character of string and continues until it
encounters a nonnumeric character. Numeric characters are digits, leading plus and minus
signs, a decimal point, and the octal and hexadecimal prefixes (&O and &H respectively).
Dollar signs and commas are not included. White space is ignored. If the function does not
recognize a number, it returns 0. Here are some examples:
Val(“55 23rd Street”) ‘ returns the value 5523
Val(“-1.12”) ‘ returns the value -1.12