Page 152 - Fair, Geyer, and Okun's Water and wastewater engineering : water supply and wastewater removal
P. 152
JWCL344_ch03_061-117.qxd 8/17/10 7:48 PM Page 114
114 Chapter 3 Water Sources: Groundwater
Distance to surface
Water
Distance to
surface water bank
Elevation
Elevation
Bottom elevation
Amount of bottom fluctuation
Depth Water elevation
Elevation Amount of water fluctuation
Depth
Elevation
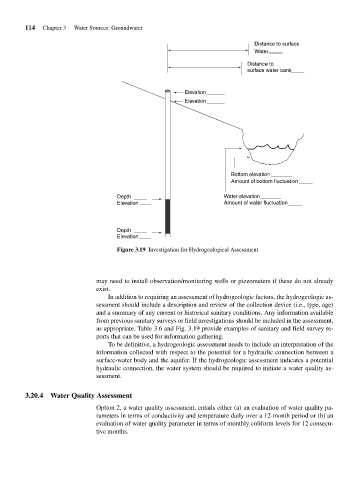
Figure 3.19 Investigation for Hydrogeological Assessment
may need to install observation/monitoring wells or piezometers if these do not already
exist.
In addition to requiring an assessment of hydrogeologic factors, the hydrogeologic as-
sessment should include a description and review of the collection device (i.e., type, age)
and a summary of any current or historical sanitary conditions. Any information available
from previous sanitary surveys or field investigations should be included in the assessment,
as appropriate. Table 3.6 and Fig. 3.19 provide examples of sanitary and field survey re-
ports that can be used for information gathering.
To be definitive, a hydrogeologic assessment needs to include an interpretation of the
information collected with respect to the potential for a hydraulic connection between a
surface-water body and the aquifer. If the hydrogeologic assessment indicates a potential
hydraulic connection, the water system should be required to initiate a water quality as-
sessment.
3.20.4 Water Quality Assessment
Option 2, a water quality assessment, entails either (a) an evaluation of water quality pa-
rameters in terms of conductivity and temperature daily over a 12-month period or (b) an
evaluation of water quality parameter in terms of monthly coliform levels for 12 consecu-
tive months.