Page 95 - Fiber Bragg Gratings
P. 95
74 Chapter 3 Fabrication of Bragg Gratings
scanning beam v uv and that of the fiber v f as AA = Xv flv uv. Removal of
the chirp reduced the bandwidth of the grating from 0.23 nm to 0.1 nm
[48].
The elimination of out-of-band ghosts is important for telecommunica-
tions, while the postfabrication repair of expensive phase masks is very
useful for fabrication.
3.1.6 The Lloyd mirror and prism interferometer
In the double mirror arrangement of the interferometer shown in Fig. 3.1
the incident beam is split into two, and fringes form from interference
between identical copies of the incident radiation. Any phase distortion
across the input beam is automatically compensated for at the fringe
plane, or can be compensated for by the introduction phase plates, so that
local visibility of the fringes remains close to unity and chirp in the period
of the fringes reduced to zero.
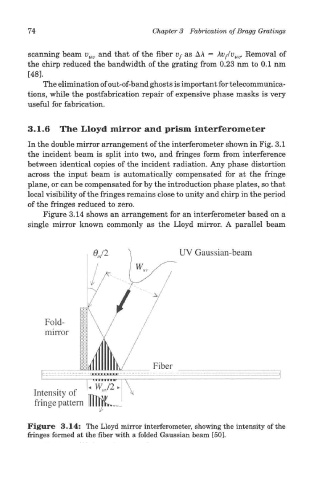
Figure 3.14 shows an arrangement for an interferometer based on a
single mirror known commonly as the Lloyd mirror. A parallel beam
Figure 3.14: The Lloyd mirror interferometer, showing the intensity of the
fringes formed at the fiber with a folded Gaussian beam [50].