Page 84 - Flexible Robotics in Medicine
P. 84
68 Chapter 3
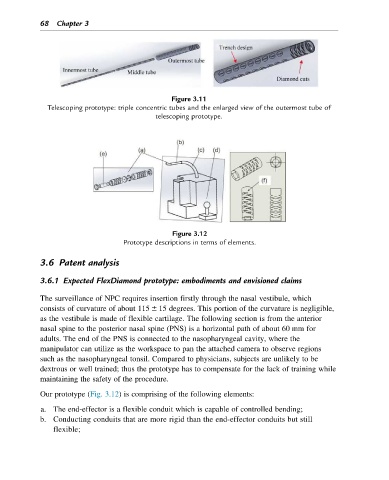
Figure 3.11
Telescoping prototype: triple concentric tubes and the enlarged view of the outermost tube of
telescoping prototype.
Figure 3.12
Prototype descriptions in terms of elements.
3.6 Patent analysis
3.6.1 Expected FlexDiamond prototype: embodiments and envisioned claims
The surveillance of NPC requires insertion firstly through the nasal vestibule, which
consists of curvature of about 115 6 15 degrees. This portion of the curvature is negligible,
as the vestibule is made of flexible cartilage. The following section is from the anterior
nasal spine to the posterior nasal spine (PNS) is a horizontal path of about 60 mm for
adults. The end of the PNS is connected to the nasopharyngeal cavity, where the
manipulator can utilize as the workspace to pan the attached camera to observe regions
such as the nasopharyngeal tonsil. Compared to physicians, subjects are unlikely to be
dextrous or well trained; thus the prototype has to compensate for the lack of training while
maintaining the safety of the procedure.
Our prototype (Fig. 3.12) is comprising of the following elements:
a. The end-effector is a flexible conduit which is capable of controlled bending;
b. Conducting conduits that are more rigid than the end-effector conduits but still
flexible;