Page 241 - Fluid-Structure Interactions Slender Structure and Axial Flow (Volume 1)
P. 241
222 SLENDER STRUCTURES AND AXIAL FLOW
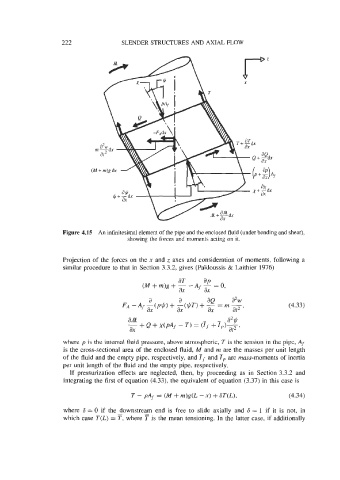
Figure 4.15 An infinitesimal element of the pipe and the enclosed fluid (under bending and shear),
showing the forces and moments acting on it.
Projection of the forces on the x and z axes and consideration of moments, following a
similar procedure to that in Section 3.3.2, gives (Paidoussis & Laithier 1976)
a a aQ a2w
FA -Af -(p11,) + -($T) + - = m -, (4.33)
ax ax ax at2
where p is the internal fluid pressure, above atmospheric, T is the tension in the pipe, AJ
is the cross-sectional area of the enclosed fluid, M and rn are the masses per unit length
of the fluid and the empty pipe, respectively, and ?J and Tp are mass-moments of inertia
per unit length of the fluid and the empty pipe, respectively.
If pressurization effects are neglected, then, by proceeding as in Section 3.3.2 and
integrating the first of equation (4.33), the equivalent of equation (3.37) in this case is
T - PAJ = (M f rn)g(L - x) + 6T(L), (4.34)
where 6 = 0 if the downstream end is free to slide axially and 6 = 1 if it is not, in
which case T(L) = T, where T is the mean tensioning. In the latter case, if additionally