Page 89 - Fluid Catalytic Cracking Handbook
P. 89
§§ Fluid Catalytic Cracking Handbook
allows vanadium to find zeolite sites. This deactivation is in
addition to the hydrothermal deactivation caused by higher
regenerator temperature alone.
3. Combustion Mode
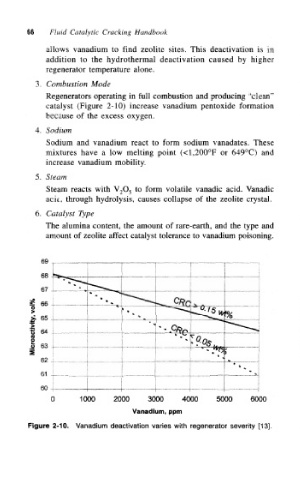
Regenerators operating in full combustion and producing "clean"
catalyst (Figure 2-10) increase vanadium pentoxide formation
because of the excess oxygen.
4. Sodium
Sodium and vanadium react to form sodium vanadates. These
mixtures have a low melting point (<1,200°F or 649°C) and
increase vanadium mobility.
5. Steam
Steam reacts with V 2O 5 to form volatile vanadic acid. Vanadic
acid, through hydrolysis, causes collapse of the zeolite crystal.
6. Catalyst Type
The alumina content, the amount of rare-earth, and the type and
amount of zeolite affect catalyst tolerance to vanadium poisoning.
80 4-_________) j. [_ I ]_
0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000
Vanadium, ppm
Figure 2-10. Vanadium deactivation varies with regenerator severity [13].