Page 99 - Fluid Catalytic Cracking Handbook
P. 99
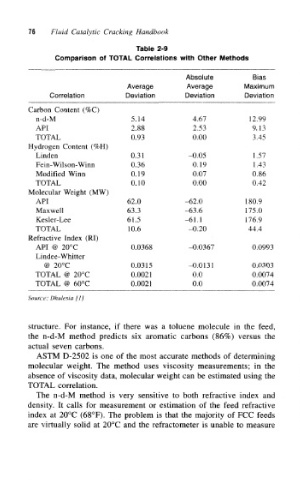
76 Fluid Catalytic Cracking Handbook
Table 2-9
Comparison of TOTAL Correlations with Other Methods
Absolute Bias
Average Average Maximum
Correlation Deviation Deviation Deviation
Carbon Content (%C)
n-d-M 5.14 4.67 12.99
API 2.88 2.53 9.13
TOTAL 0.93 0.00 3.45
Hydrogen Content (%H)
Linden 0.31 -0.05 1.57
Fein-Wilson-Winn 0.36 0.19 1.43
Modified Winn 0.19 0.07 0.86
TOTAL 0.10 0.00 0.42
Molecular Weight (MW)
API 62.0 -62.0 180.9
Maxwell 63.3 -63.6 175.0
Kesler-Lee 61.5 -61.1 176.9
TOTAL 10.6 -0.20 44.4
Refractive Index (RI)
API @ 20°C 0.0368 -0.0367 0.0993
Lindee-Whitter
@ 20°C 0.0315 -0.0131 0.0303
TOTAL @ 20°C 0.0021 0.0 0.0074
TOTAL @ 60°C 0.0021 0.0 0.0074
Source: Dhuleaia [1]
structure. For instance, if there was a toluene molecule in the feed,
the n-d-M method predicts six aromatic carbons (86%) versus the
actual seven carbons.
ASTM D-2502 is one of the most accurate methods of determining
molecular weight. The method uses viscosity measurements; in the
absence of viscosity data, molecular weight can be estimated using the
TOTAL correlation.
The n-d-M method is very sensitive to both refractive index and
density. It calls for measurement or estimation of the feed refractive
index at 20°C (68°F). The problem is that the majority of FCC feeds
are virtually solid at 20°C and the refractometer is unable to measure