Page 460 - Forensic Structural Engineering Handbook
P. 460
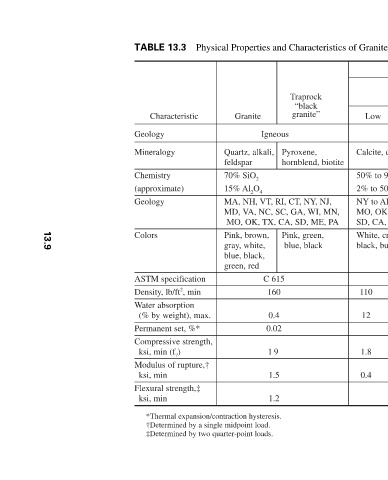
Sandstone
Physical Properties and Characteristics of Granite, Limestone, and Sandstone
Limestone
Density
Low Quartzitic Quartzitic sandstone Sandstone High Medium Sedimentary Quartz, feldspar Calcite, dolomite SiO 2 NaAlS 2 O 4 50% to 97% CaCO 4 KAlS 2 O 4 CaAlS 2 O 4 2% to 50% MgCO 4 Most states NY to AL, IN to MS, IA, NE, KS, MO, OK, AR, TX, WI, CO, SD, CA, MN, WY Brown, gray, rose, cre
Traprock “black granite” Pyroxene, hornblend, biotite Pink, green, blue, black
Igneous MA, NH, VT, RI, CT, NY, NJ, MD, VA, NC, SC, GA, WI, MN, MO, OK, TX, CA, SD, ME, PA C 615 160 0.4 0.02 1 9 1.5 1.2
Granite Quartz, alkali, feldspar 70% SiO 2 15% Al 2 O 4 Pink, brown, gray, white, blue, black, green, red *Thermal expansion/contraction hysteresis. †Determined by a single midpoint load. ‡Determined by two quarter-point loads.
TABLE 13.3 Characteristic Geology Mineralogy Chemistry (approximate) Geology Colors ASTM specification Density, lb/ft 2 , min Water absorption (% by weight), max. Permanent set, %* Compressive strength, ksi, min (f ? ) Modulus of rupture,† ksi, min Flexural strength,‡ ksi, min
13.9