Page 223 - Formation Damage during Improved Oil Recovery Fundamentals and Applications
P. 223
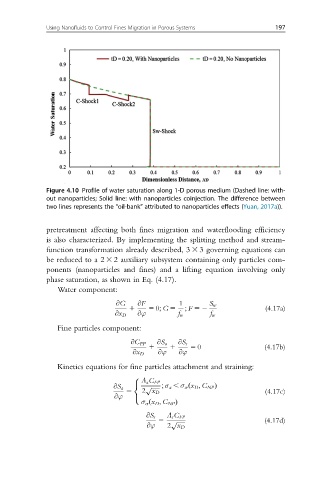
Using Nanofluids to Control Fines Migration in Porous Systems 197
Figure 4.10 Profile of water saturation along 1-D porous medium (Dashed line: with-
out nanoparticles; Solid line: with nanoparticles coinjection. The difference between
two lines represents the “oil-bank” attributed to nanoparticles effects (Yuan, 2017a)).
pretreatment affecting both fines migration and waterflooding efficiency
is also characterized. By implementing the splitting method and stream-
function transformation already described, 3 3 3 governing equations can
be reduced to a 2 3 2 auxiliary subsystem containing only particles com-
ponents (nanoparticles and fines) and a lifting equation involving only
phase saturation, as shown in Eq. (4.17).
Water component:
@G @F 1 S w
1 5 0; G 5 ; F 52 (4.17a)
@x D @ϕ f w f w
Fine particles component:
@C FP @S a @S s
1 1 5 0 (4.17b)
@x D @ϕ @ϕ
Kinetics equations for fine particles attachment and straining:
8
Λ a C FP
ð
< ffiffiffiffiffiffi ; σ a , σ cr x D ; C NP Þ
@S a 5 p (4.17c)
@ϕ : 2 x D
ð
σ cr x D ; C NP Þ
@S s Λ s C FP (4.17d)
@ϕ 5 p ffiffiffiffiffiffi
2 x D