Page 89 - Formation Damage during Improved Oil Recovery Fundamentals and Applications
P. 89
Formation Damage by Fines Migration: Mathematical and Laboratory Modeling, Field Cases 71
Straining
Grain
Migration Detachment
F L
F L
F d
F d
Attached F g
F g F e
particles
F e
Grain
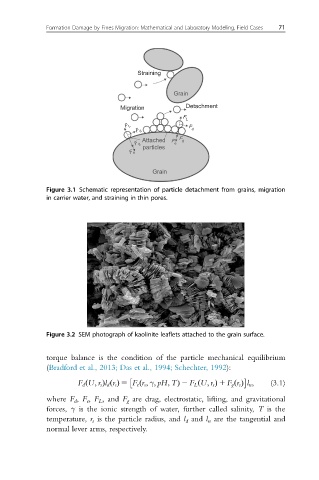
Figure 3.1 Schematic representation of particle detachment from grains, migration
in carrier water, and straining in thin pores.
Figure 3.2 SEM photograph of kaolinite leaflets attached to the grain surface.
torque balance is the condition of the particle mechanical equilibrium
(Bradford et al., 2013; Das et al., 1994; Schechter, 1992):
ð
F d U; r s Þl d r s ðÞ 5 F e r s ; γ; pH; Tð Þ 2 F L U; r s Þ 1 F g r s ðÞ l n ; (3.1)
ð
where F d , F e , F L , and F g are drag, electrostatic, lifting, and gravitational
forces, γ is the ionic strength of water, further called salinity, T is the
temperature, r s is the particle radius, and l d and l n are the tangential and
normal lever arms, respectively.