Page 204 - From Smart Grid to Internet of Energy
P. 204
180 From smart grid to internet of energy
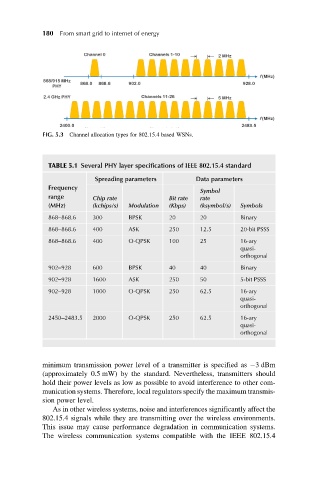
FIG. 5.3 Channel allocation types for 802.15.4 based WSNs.
TABLE 5.1 Several PHY layer specifications of IEEE 802.15.4 standard
Spreading parameters Data parameters
Frequency
Symbol
range Chip rate Bit rate rate
(MHz) (kchips/s) Modulation (Kbps) (ksymbol/s) Symbols
868–868.6 300 BPSK 20 20 Binary
868–868.6 400 ASK 250 12.5 20-bit PSSS
868–868.6 400 O-QPSK 100 25 16-ary
quasi-
orthogonal
902–928 600 BPSK 40 40 Binary
902–928 1600 ASK 250 50 5-bit PSSS
902–928 1000 O-QPSK 250 62.5 16-ary
quasi-
orthogonal
2450–2483.5 2000 O-QPSK 250 62.5 16-ary
quasi-
orthogonal
minimum transmission power level of a transmitter is specified as 3 dBm
(approximately 0.5 mW) by the standard. Nevertheless, transmitters should
hold their power levels as low as possible to avoid interference to other com-
munication systems. Therefore, local regulators specify the maximum transmis-
sion power level.
As in other wireless systems, noise and interferences significantly affect the
802.15.4 signals while they are transmitting over the wireless environments.
This issue may cause performance degradation in communication systems.
The wireless communication systems compatible with the IEEE 802.15.4