Page 248 - Fundamentals of Air Pollution 3E
P. 248
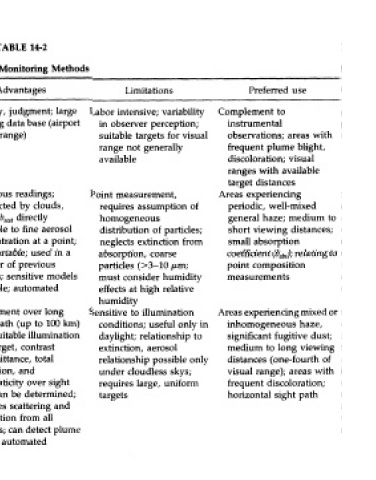
TABLE 14-2
Visibility Monitoring Methods
Method Parameters measured Advantages Limitations Preferred use
iuman observer Perceived visual quality, Flexibility, judgment; large Labor intensive; variability Complement to
atmospheric color, plume existing data base (airport in observer perception; instrumental
blight, visual range visual range) suitable targets for visual observations; areas with
range not generally frequent plume blight,
available discoloration; visual
ranges with available
target distances
ntegrating nephelometer Scattering coefficient (b^t) at Continuous readings; Point measurement, Areas experiencing
site unaffected by clouds, requires assumption of periodic, well-mixed
night; b^ directly homogeneous general haze; medium to
relatable to fine aerosol distribution of particles; short viewing distances;
concentration at a point; neglects extinction from small absorption
semiportable; used in a absorption, coarse coefficient (b^); relating to
number of previous particles (>3-10 j*,m; point composition
studies; sensitive models must consider humidity measurements
available; automated effects at high relative
humidity
Vlultiwavelength Sky and/or target radiance, Measurement over long Sensitive to illumination Areas experiencing mixed or
telephotometer contrast at various view path (up to 100 km) conditions; useful only in inhomogeneous haze,
wavelengths with suitable illumination daylight; relationship to significant fugitive dust;
and target, contrast extinction, aerosol medium to long viewing
transmittance, total relationship possible only distances (one-fourth of
extinction, and under cloudless skys; visual range); areas with
chromaticity over sight requires large, uniform frequent discoloration;
path can be determined; targets horizontal sight path
includes scattering and
absorption from all
sources; can detect plume
blight; automated