Page 339 - Fundamentals of Air Pollution 3E
P. 339
II. Turbulence 295
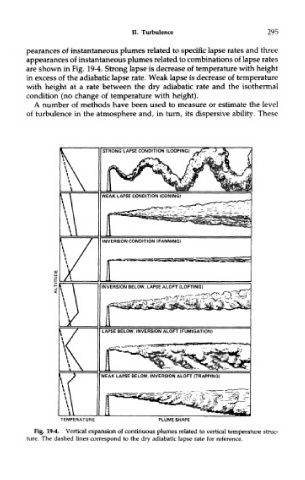
pearances of instantaneous plumes related to specific lapse rates and three
appearances of instantaneous plumes related to combinations of lapse rates
are shown in Fig. 19-4. Strong lapse is decrease of temperature with height
in excess of the adiabatic lapse rate. Weak lapse is decrease of temperature
with height at a rate between the dry adiabatic rate and the isothermal
condition (no change of temperature with height).
A number of methods have been used to measure or estimate the level
of turbulence in the atmosphere and, in turn, its dispersive ability. These
Fig. 19-4. Vertical expansion of continuous plumes related to vertical temperature struc-
ture. The dashed lines correspond to the dry adiabatic lapse rate for reference.