Page 115 - Fundamentals of Air Pollution
P. 115
III. Stationary Sources 85
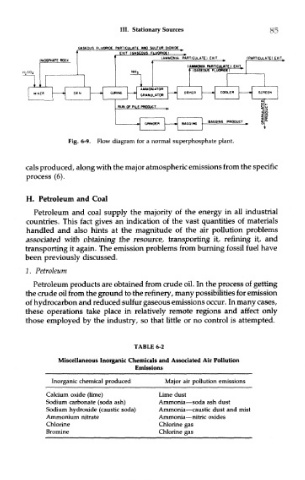
Fig. 6-9. Flow diagram for a normal superphosphate plant.
cals produced, along with the major atmospheric emissions from the specific
process (6).
H. Petroleum and Coal
Petroleum and coal supply the majority of the energy in all industrial
countries. This fact gives an indication of the vast quantities of materials
handled and also hints at the magnitude of the air pollution problems
associated with obtaining the resource, transporting it, refining it, and
transporting it again. The emission problems from burning fossil fuel have
been previously discussed.
1. Petroleum
Petroleum products are obtained from crude oil. In the process of getting
the crude oil from the ground to the refinery, many possibilities for emission
of hydrocarbon and reduced sulfur gaseous emissions occur. In many cases,
these operations take place in relatively remote regions and affect only
those employed by the industry, so that little or no control is attempted.
TABLE 6-2
Miscellaneous Inorganic Chemicals and Associated Air Pollution
Emissions
Inorganic chemical produced Major air pollution emissions
Calcium oxide (lime) Lime dust
Sodium carbonate (soda ash) Ammonia — soda ash dust
Sodium hydroxide (caustic soda) Ammonia — caustic dust and mist
Ammonium nitrate Ammonia — nitric oxides
Chlorine Chlorine gas
Bromine Chlorine gas