Page 152 - Fundamentals of Computational Geoscience Numerical Methods and Algorithms
P. 152
6.4 Applications of the Proposed Decoupling Procedure 141
Solute Chemical
Da = Time Scale Diffusion Reaction
Dominates Dominates
for Solute
Advection/Time
Scale for
Chemical
Reaction
Chemical
Reaction
Dominates
1.0
Solute
Advection
Dominates
1.0
Z = Time scale for Solute Diffusion/Time
Scale for Chemical Reaction
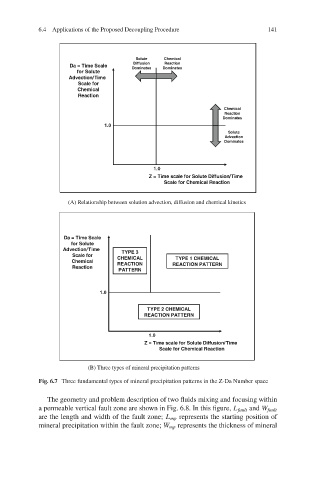
(A) Relationship between solution advection, diffusion and chemical kinetics
Da = Time Scale
for Solute
Advection/Time
TYPE 3
Scale for CHEMICAL
TYPE 1 CHEMICAL
Chemical REACTION REACTION PATTERN
Reaction
PATTERN
1.0
TYPE 2 CHEMICAL
REACTION PATTERN
1.0
Z = Time scale for Solute Diffusion/Time
Scale for Chemical Reaction
(B) Three types of mineral precipitation patterns
Fig. 6.7 Three fundamental types of mineral precipitation patterns in the Z-Da Number space
The geometry and problem description of two fluids mixing and focusing within
a permeable vertical fault zone are shown in Fig. 6.8. In this figure, L fault and W fault
are the length and width of the fault zone; L mp represents the starting position of
mineral precipitation within the fault zone; W mp represents the thickness of mineral