Page 156 - Fundamentals of Geomorphology
P. 156
SMALL-SCALE TECTONIC AND STRUCTURAL LANDFORMS 139
Ice
Proglacial
drainage
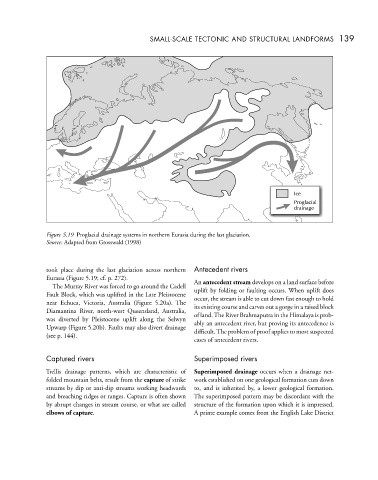
Figure 5.19 Proglacial drainage systems in northern Eurasia during the last glaciation.
Source: Adapted from Grosswald (1998)
took place during the last glaciation across northern Antecedent rivers
Eurasia (Figure 5.19; cf. p. 272). An antecedent stream develops on a land surface before
The Murray River was forced to go around the Cadell
Fault Block, which was uplifted in the Late Pleistocene uplift by folding or faulting occurs. When uplift does
occur, the stream is able to cut down fast enough to hold
near Echuca, Victoria, Australia (Figure 5.20a). The its existing course and carves out a gorge in a raised block
Diamantina River, north-west Queensland, Australia, of land.The River Brahmaputra in the Himalaya is prob-
was diverted by Pleistocene uplift along the Selwyn
Upwarp (Figure 5.20b). Faults may also divert drainage ably an antecedent river, but proving its antecedence is
difficult.The problem of proof applies to most suspected
(see p. 144).
cases of antecedent rivers.
Captured rivers Superimposed rivers
Trellis drainage patterns, which are characteristic of Superimposed drainage occurs when a drainage net-
folded mountain belts, result from the capture of strike work established on one geological formation cuts down
streams by dip or anti-dip streams working headwards to, and is inherited by, a lower geological formation.
and breaching ridges or ranges. Capture is often shown The superimposed pattern may be discordant with the
by abrupt changes in stream course, or what are called structure of the formation upon which it is impressed.
elbows of capture. A prime example comes from the English Lake District