Page 105 - Fundamentals of Physical Volcanology
P. 105
9780632054435_4_006.qxd 12/10/2007 12:22PM Page 82
82 CHAPTER 6
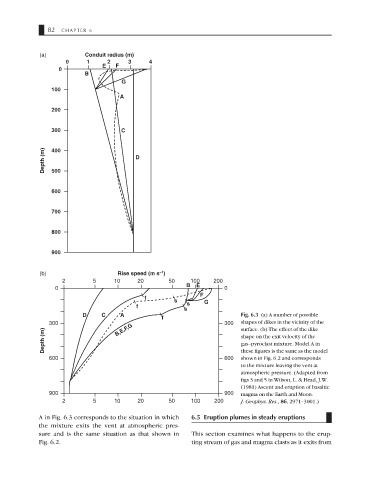
(a) Conduit radius (m)
0 1 2 3 4
0 E F
B
G
100
A
200
300 C
Depth (m) 400 D
500
600
700
800
900
(b) Rise speed (m s )
–1
2 5 10 20 50 100 200
B E
0 0
f s F
f s G
s
D C A Fig. 6.3 (a) A number of possible
f
300 B,E,F,G 300 shapes of dikes in the vicinity of the
surface. (b) The effect of the dike
Depth (m) shape on the exit velocity of the
gas–pyroclast mixture. Model A in
600 600 these figures is the same as the model
shown in Fig. 6.2 and corresponds
to the mixture leaving the vent at
atmospheric pressure. (Adapted from
figs 3 and 5 in Wilson, L. & Head, J.W.
(1981) Ascent and eruption of basaltic
900 900 magma on the Earth and Moon.
2 5 10 20 50 100 200 J. Geophys. Res., 86, 2971–3001.)
A in Fig. 6.3 corresponds to the situation in which 6.5 Eruption plumes in steady eruptions
the mixture exits the vent at atmospheric pres-
sure and is the same situation as that shown in This section examines what happens to the erup-
Fig. 6.2. ting stream of gas and magma clasts as it exits from