Page 207 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 207
Effect of Gas Wettability on Capillaries CHAPTER 5 191
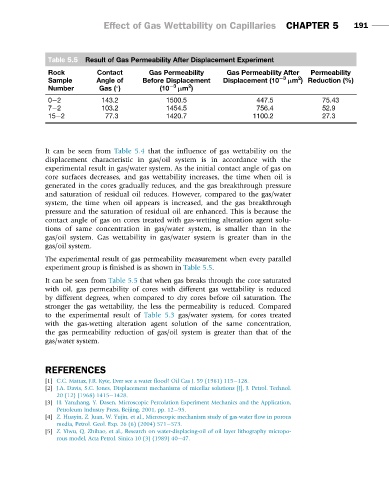
Table 5.5 Result of Gas Permeability After Displacement Experiment
Rock Contact Gas Permeability Gas Permeability After Permeability
2
Sample Angle of Before Displacement Displacement (10 23 µm ) Reduction (%)
2
Number Gas ( ) (10 23 µm )
0 2 143.2 1500.5 447.5 75.43
7 2 103.2 1454.5 756.4 52.9
15 2 77.3 1420.7 1100.2 27.3
It can be seen from Table 5.4 that the influence of gas wettability on the
displacement characteristic in gas/oil system is in accordance with the
experimental result in gas/water system. As the initial contact angle of gas on
core surfaces decreases, and gas wettability increases, the time when oil is
generated in the cores gradually reduces, and the gas breakthrough pressure
and saturation of residual oil reduces. However, compared to the gas/water
system, the time when oil appears is increased, and the gas breakthrough
pressure and the saturation of residual oil are enhanced. This is because the
contact angle of gas on cores treated with gas-wetting alteration agent solu-
tions of same concentration in gas/water system, is smaller than in the
gas/oil system. Gas wettability in gas/water system is greater than in the
gas/oil system.
The experimental result of gas permeability measurement when every parallel
experiment group is finished is as shown in Table 5.5.
It can be seen from Table 5.5 that when gas breaks through the core saturated
with oil, gas permeability of cores with different gas wettability is reduced
by different degrees, when compared to dry cores before oil saturation. The
stronger the gas wettability, the less the permeability is reduced. Compared
to the experimental result of Table 5.3 gas/water system, for cores treated
with the gas-wetting alteration agent solution of the same concentration,
the gas permeability reduction of gas/oil system is greater than that of the
gas/water system.
REFERENCES
[1] C.C. Mattax, J.R. Kyte, Ever see a water flood? Oil Gas J. 59 (1961) 115 128.
[2] J.A. Davis, S.C. Jones, Displacement mechanisms of micellar solutions [J], J. Petrol. Technol.
20 (12) (1968) 1415 1428.
[3] H. Yanzhang, Y. Dasen, Microscopic Percolation Experiment Mechanics and the Application,
Petroleum Industry Press, Beijing, 2001, pp. 12 95.
[4] Z. Huayin, Z. Juan, W. Yujin, et al., Microscopic mechanism study of gas-water flow in porous
media, Petrol. Geol. Exp. 26 (6) (2004) 571 573.
[5] Z. Yiwu, Q. Zhihao, et al., Research on water-displacing-oil of oil layer lithography micropo-
rous model, Acta Petrol. Sinica 10 (3) (1989) 40 47.