Page 19 - Gas Adsorption Equilibria
P. 19
4
literature [0.7-0.13] and expert programs for gas separation process design
[0.20], [0.21].
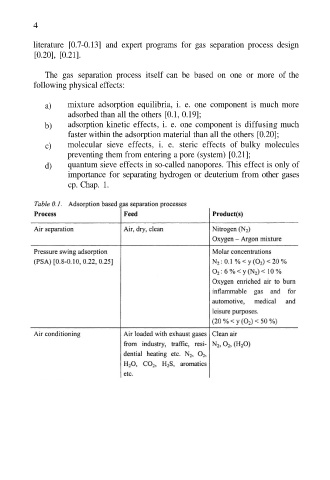
The gas separation process itself can be based on one or more of the
following physical effects:
a) mixture adsorption equilibria, i. e. one component is much more
adsorbed than all the others [0.1, 0.19];
b) adsorption kinetic effects, i. e. one component is diffusing much
faster within the adsorption material than all the others [0.20];
c) molecular sieve effects, i. e. steric effects of bulky molecules
preventing them from entering a pore (system) [0.21];
d) quantum sieve effects in so-called nanopores. This effect is only of
importance for separating hydrogen or deuterium from other gases
cp. Chap. 1.