Page 41 - Geology of Carbonate Reservoirs
P. 41
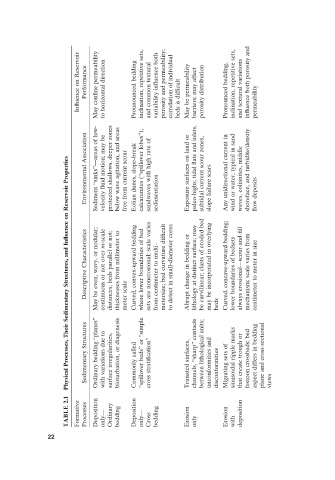
Influence on Reservoir Performance ne permeability May confi to horizontal direction Prounounced bedding inclination, repetitive sets, and common textural uence both variability infl porosity and permeability; correlation of individual cult beds is diffi May be permeability barriers; may affect porosity distribution Pronounced bedding,
Environmental Association Sediment “ sinks ” — areas of low - velocity fluid motion; may be protected shallows, deeper zones below wave agitation, and areas free from current scour Eolian dunes, slope - break “ spillover lobes ” ), calcarenites ( sandwaves with high rate of sedimentation Exposure surfaces on land or paleo - highs, tidal flats and i
Physical Processes, Their Sedimentary Structures, and Influence on Reservoir Properties
Descriptive Characteristics May be even, wavy, or nodular; continuous or not over distances; beds parallel or not; thicknesses from millimeter to meter scale Curved, convex - upward bedding where lower boundaries of bed sets are nonerosional; scale varies from centimeter to multi metersize; bed curvature diffi to detect in small Abrupt change in beddin
m - scale - cult - diameter cores - upward bedding; ll fl
Sedimentary Structures Ordinary bedding “ planes ” with variations due to surface irregularities, bioturbation, or diagenesis Commonly called “ spillover beds ” or “ simple cross stratification ” Trunated surfaces, channels, “ sharp ” contacts between lithological units; unconformities and disconformities Migrating sets
views
TABLE 2.1 Formative Processes Deposition only — Ordinary bedding Deposition only — Cross bedding Erosion only Erosion with deposition
22