Page 67 - Geology of Carbonate Reservoirs
P. 67
48 CARBONATE RESERVOIR ROCK PROPERTIES
for further analysis. Detailed descriptions of the wide variety of logging devices,
logging principles, and methods of interpretation are beyond the scope and purpose
of this book, but a list of typical logs in use today, along with a brief list of their
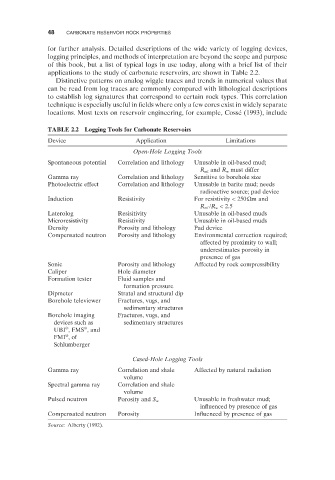
applications to the study of carbonate reservoirs, are shown in Table 2.2 .
Distinctive patterns on analog wiggle traces and trends in numerical values that
can be read from log traces are commonly compared with lithological descriptions
to establish log signatures that correspond to certain rock types. This correlation
technique is especially useful in fields where only a few cores exist in widely separate
locations. Most texts on reservoir engineering, for example, Coss é (1993) , include
TABLE 2.2 Logging Tools for Carbonate Reservoirs
Device Application Limitations
Open - Hole Logging Tools
Spontaneous potential Correlation and lithology Unusable in oil - based mud;
R mf and R w must differ
Gamma ray Correlation and lithology Sensitive to borehole size
Photoelectric effect Correlation and lithology Unusable in barite mud; needs
radioactive source; pad device
Induction Resistivity For resistivity < 250 Ω m and
R mf / R w < 2.5
Laterolog Resisitivity Unusable in oil - based muds
Microresistivity Resistivity Unusable in oil - based muds
Density Porosity and lithology Pad device
Compensated neutron Porosity and lithology Environmental correction required;
affected by proximity to wall;
underestimates porosity in
presence of gas
Sonic Porosity and lithology Affected by rock compressibility
Caliper Hole diameter
Formation tester Fluid samples and
formation pressure
Dipmeter Stratal and structural dip
Borehole televiewer Fractures, vugs, and
sedimentary structures
Borehole imaging Fractures, vugs, and
devices such as sedimentary structures
®
®
UBI , FMS , and
®
FMI , of
Schlumberger
Cased - Hole Logging Tools
Gamma ray Correlation and shale Affected by natural radiation
volume
Spectral gamma ray Correlation and shale
volume
Pulsed neutron Porosity and S w Unusable in freshwater mud;
influenced by presence of gas
Compensated neutron Porosity Influenced by presence of gas
Source: Alberty (1992) .