Page 98 - Geology of Carbonate Reservoirs
P. 98
CARBONATE DEPOSITIONAL PLATFORMS 79
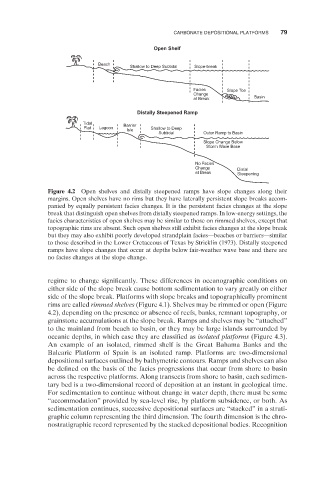
Open Shelf
Beach
Shallow to Deep Subtidal Slope-break
Facies Slope Toe
Change
at Break Basin
Distally Steepened Ramp
Tidal Barrier
Flat Lagoon Shallow to Deep
Isle
Subtidal Outer Ramp to Basin
Slope Change Below
Storm Wave Base
No Facies
Change Distal
at Break Steepening
Figure 4.2 Open shelves and distally steepened ramps have slope changes along their
margins. Open shelves have no rims but they have laterally persistent slope breaks accom-
panied by equally persistent facies changes. It is the persistent facies changes at the slope
break that distinguish open shelves from distally steepened ramps. In low - energy settings, the
facies characteristics of open shelves may be similar to those on rimmed shelves, except that
topographic rims are absent. Such open shelves still exhibit facies changes at the slope break
but they may also exhibit poorly developed strandplain facies — beaches or barriers — similar
to those described in the Lower Cretaceous of Texas by Stricklin (1973) . Distally steepened
ramps have slope changes that occur at depths below fair - weather wave base and there are
no facies changes at the slope change.
regime to change significantly. These differences in oceanographic conditions on
either side of the slope break cause bottom sedimentation to vary greatly on either
side of the slope break. Platforms with slope breaks and topographically prominent
rims are called rimmed shelves (Figure 4.1 ). Shelves may be rimmed or open (Figure
4.2 ), depending on the presence or absence of reefs, banks, remnant topography, or
grainstone accumulations at the slope break. Ramps and shelves may be “ attached ”
to the mainland from beach to basin, or they may be large islands surrounded by
oceanic depths, in which case they are classified as isolated platforms (Figure 4.3 ).
An example of an isolated, rimmed shelf is the Great Bahama Banks and the
Balearic Platform of Spain is an isolated ramp. Platforms are two - dimensional
depositional surfaces outlined by bathymetric contours. Ramps and shelves can also
be defined on the basis of the facies progressions that occur from shore to basin
across the respective platforms. Along transects from shore to basin, each sedimen-
tary bed is a two - dimensional record of deposition at an instant in geological time.
For sedimentation to continue without change in water depth, there must be some
“ accommodation ” provided by sea - level rise, by platform subsidence, or both. As
sedimentation continues, successive depositional surfaces are “ stacked ” in a strati-
graphic column representing the third dimension. The fourth dimension is the chro-
nostratigraphic record represented by the stacked depositional bodies. Recognition